Law on video recording cameras on roads
The use of video recording cameras leads to abuses by inspectors. The reason for this permissiveness is the absence in the laws of the Russian Federation of unambiguous rules for the installation and use of radars. The Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation deals superficially with fasteners and contains the following information:
- camera readings must be reflected in the protocol on violation of traffic rules;
- if the camera was installed illegally, then the information received through it is invalid;
- stationary automatic fixation devices are accompanied by special signs.
The requirements for radars and the procedure for their use do not have an exhaustive description. Fragmentary information about them in various laws sometimes contradicts each other.
Where you cannot install photo and video cameras
An entrepreneur does not have the right to install video recording systems at his own discretion. According to Art. 57 of the Traffic Regulations, installation sites for stationary automatic fixing equipment must be designated by the leadership of the State Traffic Inspectorate; most often these are emergency sections of roads. The place and time of use of mobile systems is determined by the head of the unit on the procedure for the employee to perform duty. The same article states that automatic fixation equipment cannot be used in places where traffic restrictions are established by temporary road signs. Thus, in the area of temporary signs (for example, placed during repair work), automatic photo and video recording is prohibited, that is, a motorist who received a fine in this area can report to the traffic police or the prosecutor's office with a statement about the incorrect location of the equipment.
According to Russian legislation, drivers must be warned about the presence of a complex on the route that records violations with a special sign. Such warning signs must be placed on all stationary means of photo and video recording, while GOST does not provide for the installation of such warnings on mobile systems. In fact, the purpose of installing the complexes is not to enrich themselves at the expense of drivers, but to reduce the number of accidents and traffic violations. Every day more and more eyes are closely monitoring the order on the roads, so drivers need to be extremely careful while driving - this will not only ensure safety, but will also save them from unnecessary costs of paying fines.
The business of video cameras recording traffic violations has appeared relatively recently. It consists not simply in installing the necessary equipment, but in its direct use for issuing fines and receiving a certain reward for this. We will talk about the prerequisites, legislative features and other important points of this format of earning money in the article.
Types of cameras
Cameras are divided into three types according to format:
- stationary;
- portable;
- mobile.
BINAR. A compact video recording camera that fits into the interior of a patrol car. The device is equipped with a program through which data is downloaded to a computer and printed. When the shift ends, the traffic police officer moves all the information from the camera to a common database.
LISD-2F. The laser complex is installed on a tripod next to the official vehicle, and can also be in the hands of the inspector. The device is used in manual mode and supports electronic media.
CHRIS P. Mobile automatic complex that works without an operator. A wireless communication channel allows the device to send data about violations to a computer in real time. Information is saved to the energy carrier automatically.
PARKON. The fixer specializes in drivers who violate parking rules. The data received from the device is processed at the central station. The device consists of a removable handle and two cameras.
What violations does the camera record?
In addition to recording speed limit violations, modern cameras can capture other offenses, for example:
- if the driver parked his car in the wrong place;
- if the driver did not let pedestrians pass in the pedestrian crossing area;
- if the driver entered the oncoming lane or crossed a solid marking line on the roadway;
- if the driver drove onto a section of the road located in the area of prohibition signs;
- if the driver violated traffic rules while driving through a controlled intersection or railway crossing;
- if the car is moving in a specially designated lane for public transport or bicycles, along the side of the road or along tram tracks;
- if the driver ran a red traffic light or drove beyond the stop line;
- if the driver and/or front seat passenger are not wearing seat belts or are talking on a mobile phone while driving;
- if the vehicle's lights (headlights) do not light up.
In the capital and the Moscow region, it is planned to equip almost all tunnels with photo-video recording devices. They should record the status of the lights at the beginning and end of the tunnel, however, this project is still in development due to the controversial issue of dirty headlights.
Many drivers are interested in the question: “How does a stop line camera work?” Similar to other offenses involving entry into a prohibited area, driving beyond the stop line is recorded by a camera in this way: the boundaries of the road section into which entry is considered an offense are programmed into the device. Depending on the settings, multifunctional cameras can record driving beyond the stop line as if it were running a red traffic light.
We recommend that you read additionally about traffic police fines from photo and video cameras.
How do cameras work?
Video recording devices are designed to detect exceeding speed limits. Camera capabilities also include control of:
- driving in the public transport lane;
- running a stop line or ignoring road signs;
- driving with headlights off;
- driving in the oncoming lane;
- turns from a row that does not involve this maneuver.
The number of functions varies depending on the selected device. Some devices have a narrow specialization, such as Parkon. In the future, recognition of cars with a low environmental class is expected. They will be fined in zones with restrictions on polluting vehicles.
According to the Russian State Traffic Safety Inspectorate, in 2021 the number of traffic cameras increased by 20%. In total, there are currently 15.5 thousand photo-video recording systems for traffic violations operating on the country’s roads. This figure has been formed mainly over the last decade. The experience accumulated over the years of successful work by specialists allows us to make some generalizations and reveal some nuances that can help potential customers.
First of all, according to the experts who are preparing the estimate for the future installation, any customer must clearly understand why a photo-video recording system is needed and what specific tasks it will solve. The answer to this question determines the final price of the system itself and the subsequent cost of its maintenance. The mistake many newbies make is that they want their future line of control to detect as many offenses as possible. This approach greatly increases the cost of installation, and, as a rule, three quarters of all traffic violations at this point will be of only one type. Thus, if the customer determines that there are violations, he will save money.
Each project to deploy a photo-video recording system involves the following actions:
- supply of equipment;
- design and survey work (if necessary);
- work on technological connection to electrical networks in compliance with the technical conditions of electricity suppliers;
- compliance with technical specifications of third-party organizations (if necessary);
- laying additional communications and installing supports (if necessary);
- installation work and commissioning of systems.
In addition, an automatic traffic control system is not only a computer, video camera and other hardware, but also software. The full name is just that: “hardware-software complex”. At the same time, the cost of the software directly depends on the tasks that the complex will perform. The cost of the project is also affected by the site survey. Often, a specialist visit to the site of the proposed installation is required to draw up an accurate map of the site. The situation can be complicated if the project consists of several separated control lines. Such a visit is a prerequisite if preparations are being made to install systems for measuring the speed of vehicles on the site (the so-called “average speed”). Naturally, all man-hours spent will be included in the estimate.
To find out the cost offhand, it is enough to know what type of offense this control line will detect. There is a gradation from easily provable types of violations to violations that require additional confirmation. The latter especially require the facility to be equipped with surveillance cameras. Easily provable types of traffic violations that do not require a large number of video cameras include the following control lines:
- instantaneous speed control line (about 10 thousand complexes in Russia);
- public transport lane control (706 systems);
- fixation of traffic on the side of the road (375 complexes);
- speed control on a section of road (average speed).
Next come objects where violations require additional confirmation, which means that it is necessary to install additional recognition and surveillance cameras. These include the following violations:
- turning around in prohibited places (321 complexes);
- violation of road signs and markings (634 complexes);
- driving beyond the stop line of an intersection at a prohibitory traffic light (about 1.6 thousand systems);
- driving through an intersection with a prohibitory traffic light (1.3 thousand systems in Russia);
- crossing a railway crossing with a prohibitory traffic light signal (85 systems).
To understand how difficult it is to equip such facilities, it is enough to look at the equipment diagram of a standard X-shaped four-lane intersection (Fig. 1).
Today, the most difficult thing is to equip an uncontrolled pedestrian crossing. Here, special software is required to prove the violation. To equip all facilities with such systems, long debugging and additional testing time are required before acceptance of the facility by the customer.
It is interesting that recently there has been a tendency to modernize previously installed systems, which is undoubtedly much less expensive than installing from scratch. At the same time, the modernized complex may surpass the previous installation both in technical capabilities and in the number of traffic violations recorded.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the ParkRight mobile parking control and operational search systems. The cost of such a complex, in contrast to stationary systems, mainly differs in the number of connected video units.
S. KUSOV, Head of Propaganda Department
LLC "Recognition Technologies" 107023, Moscow, st. Elektrozavodskaya, 24 OC "Preobrazhensky", office 405 tel. office: +7 (495) 785 1536 technical support: +7 (495) 255 2775 e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You must have JavaScript enabled to view it. www.recognize.ru
How should a video recording camera be positioned according to the law?
The main legal requirement for radar is its visibility . Warning signs must be installed in front of such devices. In practice, traffic police officers not only ignore this rule, but also hide the cameras. If desired, the driver has the right to prove in court the illegal placement of the camera.
The radar monitors straight sections from 50 to 60 meters . The operating instructions for this device determine the distance at which the sensor should be removed from the roadway:
- 5 meters for 3 and 4 lanes;
- 9 meters for 2 and 3 lanes;
- 13 meters for 2 lanes;
- 17 meters for 1 lane.
Reference. All operators are required to have an instrument inspection certificate. They must also have a document indicating the location of the camera, confirmed by the traffic police.
Are tripods legal?
The traffic police are in charge of only stationary video recording systems for traffic violations, which are installed by the Traffic Safety Center of the Russian Federation. These are cameras on a rigid support such as “Rapier”, “Arena”, “Chris”, “Strelka”, mounted above the roadway in sections of the road with a high accident rate. They do not change their location, are installed outside the coverage areas of temporary signs, are marked with road signs “Video recording” (8.23) and transmit data to stationary traffic police posts, from where the information flows to the traffic police administrative violation processing center.
The State Traffic Inspectorate itself does not install video cameras - their installation and maintenance are the responsibility of regional administrations, which constantly experience a shortage of financial resources for the maintenance of road safety infrastructure. Therefore, there are not enough stationary video recording cameras, and local budgets solve this problem by attracting commercial organizations: they transfer the authority to install and maintain video equipment to private commercial organizations and individual entrepreneurs on an outsourcing basis.
The transfer of functions for video recording of traffic violations is legal: according to Federal Law No. 115 “On Concession Agreements”, local government authorities have the right, under an agreement, to transfer video recording functions to commercial investors. Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs who have signed a concession agreement with municipalities purchase, install and maintain video equipment at their own expense, for which they receive the right to independently:
- record traffic violations;
- print and send photo and video recordings to violators;
- organize the payment of fines.
For performing these works, companies receive either a percentage of the amount of fines or a fixed amount of each fine paid (it is decided individually in each region). The traffic police controls the installation sites of such video cameras on the roads and endorses a work permit for each private installer.
For commercial reasons, private service organizations choose to install mobile video equipment (tripods) such as Sokol-M, Berkut, Binar, Iskra, Radius, and Vizir. These video cameras are cheaper than stationary systems, their location can be quickly changed, and they are not subject to the requirement to install a “Video recording” sign or temporary road signs. The cameras are installed in close proximity to the roadway and transmit information to mobile devices of operators, who may be in a car parked at the side of the road, or directly to the traffic police data processing center.
With such “preferential” conditions for the installation and operation of video recording cameras, the task of maintaining and improving road safety is at the very bottom of the list of priorities for a commercial service company. Many private investors see only good earnings here and violate business rules to increase profits, creating a lot of problems for car enthusiasts.
Rules for installing video recording cameras on roads
In 2021, GOST R 57144-2016 and GOST R 57145-2016, which relate to the operation of video recording cameras, came into force in Russia. The new rules include the following points:
- the devices are installed on roads with poor visibility, as well as in areas where more than 3 accidents have occurred;
- dummy cameras are installed only when a decrease in violations is recorded;
- devices with a tracking function cannot measure speed at a distance of less than 50 meters;
- the probability of license plate recognition must be at least 90%;
- The cameras are required to measure speeds in the range from 20 to 250 kilometers per hour.
Reference. Failure to comply with GOSTs will result in administrative liability.
Prerequisites for the emergence of private video recording cameras
Back in the early 90s of the last century, the market for video and even audio recording did not exist. However, the direction itself aroused interest among people who subsequently created. Gradually they expanded the range of their work to the following components that can record traffic violations by road users:
- video analytics;
- traffic control system;
- Face Control facial recognition system.
In what cases should a photo-video recording sign be installed?
It is impossible
in the laws of the Russian Federation that affect the photo and video recording sign. The traffic rules indicate that this sign can be used. However, there is no mention of the obligations of traffic police officers before the law. The installation of this sign remains at the discretion of the inspectors.
However, according to Article 26.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, evidence of a violation obtained using an incorrectly installed device is canceled. In practice, the court will be on the side of the inspector (if the proceedings reach the court).
It will be difficult to prove the illegal installation of a camera, since the law remains ambivalent. That is, inspectors “should, but are not obligated .
Private video cameras recording traffic violations
The law obliges private radar owners to comply with the following rules:
Instructions for use of video recording cameras
According to the standard operating instructions for video recording cameras, the tripod:
- can control a straight section of road up to 60 meters long with high accuracy;
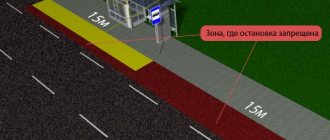
- should be on the side of the road no closer than 3 meters from the roadway;
- can be installed no further than 17 meters from a single-lane road, 13 meters from a two-lane road, 9 meters from a three-lane road and 5 meters from a four-lane road;
- must have a turning angle along a reference point parallel to the edge of the road;
- may have a speed measurement error of no more than 2 km/h.
The video camera is controlled from a mobile post by two employees (except for equipment that is fully automated and immediately transmits data to stationary traffic police posts).
Thus, the rules for installing tripods on the road are a clear list of requirements that companies servicing video equipment must comply with, since most of the rules are legislative. Compliance with the rules for installing video recording cameras allows you to work legally and transparently, ensures equal rights for road users and actually reduces the number of traffic violations.
Since most private investors involved in video recording are not inclined to follow the “rules of the game” in the pursuit of profit, their services more often cause harm on the road than help. On the other hand, violation of GOSTs, administrative regulations and operating instructions for cameras by operating companies gives competent drivers a chance to successfully appeal fines issued from video cameras and put forward counterclaims.
Rules for installing private video surveillance cameras on roads
The only rule that must be followed by owners of a private camera is the presence of a certificate . The warning signs mentioned above are rarely used by private owners.
The reason why security camera owners are still in business is because of mutual benefit. Officials do not need to spend money on purchasing equipment for traffic police patrols, and private owners receive a percentage of the fine.
By law, merchants cannot install a camera wherever they want. The list of places is approved by the State Traffic Inspectorate. However, in practice this order is often ignored. The loyal and conniving attitude of the authorities towards private owners has turned the installation of cameras into a business.
Pros and cons of doing business
At this stage, the number of traffic violations is not decreasing, which means that the business of catching motorists who flout the law is more than profitable. They earn a lot from recording cameras and the income is quite stable today, but it is important to choose the right section of road to install the equipment. It is better to organize the video recording process in places with a large number of violations, that is, on highways with active traffic, since it is simply unprofitable to spend money on expensive equipment for use on roads where there are already calm conditions.
Business benefits
The idea of making money by recording traffic violations and its implementation are made attractive to an entrepreneur by several favorable factors:
- Stable income that doesn't require much effort. To ensure this, you only need to start the process; the entrepreneur is also responsible for finding a specialist who will subsequently be involved in servicing the cameras;
- No fixed costs are expected in this business due to the long service life of the equipment;
- Funds will come from the state budget as violators pay, so you will not have to collect fines yourself;
- To receive payments, certain deadlines are established, specified in the contract;
- The business is socially oriented and, despite the dissatisfaction of many drivers, it still brings benefits to society.
Negative sides
Everything has a downside. In this case, the disadvantages are the following:
- It is possible to make a big profit only at first after installing the complex, since most often people remember in which places the cameras record speeding or other violations, and, of course, they will be law-abiding within the viewing radius of the video surveillance system. It's another matter if the equipment is mobile;
- Receipt of funds exactly on time can sometimes be inconvenient for an entrepreneur;
- It often takes a lot of time to collect fines, since not all violators pay them regularly;
- Fines can be challenged in court. To prevent this from happening, you must adhere to all standards for installing video systems;
- Relatively small amounts of commissions compared to the current amounts of fines, which in some cases can amount to hundreds of thousands of rubles;
- The contract is limited to 12 years, after which the cooperation ends.
Despite the considerable number of disadvantages, today the business is still profitable and if you have the desire and opportunity to do it, then it will not require much trouble, and the result, if you approach the matter correctly, will please you.
Legality of installing mobile cameras
Mobile radars are banned in 2021. The reason for the ban was the abuse of these devices. Inspectors were repeatedly caught extorting bribes and putting pressure on the driver. To avoid such “methods”, it was decided to “reflash” the devices. From now on, it is impossible to delete an entry made from mobile recorders after a driver has been bribed. When a traffic police officer tries to clear the device’s memory, it is blocked.
In 2021, mobile cameras continue to be used, but with some limitations. For example, at the end of a shift, devices are sealed to prevent access to the memory card. Also, this decision does not apply to Moscow and the region. The use of mobile restraints is still prohibited in these territories. Regional police use devices only as directed by management.
Law banning CCTV cameras on roads
In July, it became known about a bill that proposes banning private cameras on the roads. This amendment is intended to protect drivers from individuals who misuse private video devices.
Private owners are interested in installing cameras because they receive a percentage of the fines issued. Therefore, an increase in traffic violations is in their interests.
You can distort instrument readings in the following ways:
- artificial increase in error;
- Incorrect installation of cameras.
The authors of the bill propose to make the following changes to Article 2.6.1 of the Administrative Code:
- automatic fixation complexes must be the property of the Russian Federation or its constituent entities;
- presenting requirements for cameras and marking their installation locations is transferred to the Government of the Russian Federation.
How it works
The bill, adopted in 2014 by the Federation Council and the State Duma, provides for mutually beneficial cooperation between an entrepreneur (individual or legal entity) and government agencies. Money for equipping with equipment and its maintenance is not spent from the state budget, which is replenished, and the activity brings profit to the investor in the form of funds from fines. The idea was implemented to increase the level of safety on the roads, and a “side effect” of a good goal was quite a good income, since traffic rules have always been violated and even impressive fines cannot affect this on a large scale. Private cameras are installed to hold drivers accountable in accordance with the norms of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation; they operate in accordance with Articles 26.8 and 2.6.1 of the Code. According to the regulations, measuring instruments are required to undergo certification and metrological testing; only then the information obtained from them can be a reason for punishing the culprit. Fines will be directed to the owner of the vehicle, so if another person was driving, the owner of the vehicle will need to prove his non-involvement.
Thus, violations recorded by private video recording means legally serve as a reason for issuing a fine to the driver caught on camera “in the act”, and in some cases, for depriving the driver’s license. According to this principle, video systems were previously installed on toll roads, but now the complexes have already moved en masse to public highways. To organize a business related to traffic police video cameras, it is necessary to conclude a contract with local authorities to equip roads with systems for recording violations and their maintenance. After installing and configuring the complex, the entrepreneur receives regular income from the violators caught on camera. In this case, the fine is initially paid to the state treasury, from where a certain amount, which is part of it (the exact figures are stated in the agreement of the parties, the profit can reach 233 rubles for each fine) goes to the account of the owner of the equipment.
In what places should you not install photo/video cameras?
At the legislative level, a list of requirements for the location of radars has not been developed. As can be seen above, even the need for an appropriate sign is controversial. However, the driver has the right to challenge the fine in the following cases:
- the camera was installed on the side of the road;
- the device was deliberately hidden in the bushes;
- the clamp was too close to the lane along which the car was driving;
- the radar was not accompanied by an information sign.
Reference. At the moment, deputies are making proposals to develop rules for installing photo and video recording cameras.
GOST standards for video equipment
In order to bring the activities of private organizations providing video recording services for traffic violations to uniform rules, from 2021 the Russian Federation introduced GOSTs R 57144–2016 and R 57145–2016 regulating technical requirements for video equipment. According to these federal standards, video recording cameras must:
- have a radar, inductive, piezoelectric, magnetic or laser operating principle;
- fix speed 20-250 km/h;
- recognize license plates in any weather and time of day with a probability of at least 90%;
- capture the distinctive features of any car in a photo;
- be technically sound and free from defects;
- measure the speed of a car at a distance of no closer than 50 meters, if equipped with a tracking option (fixing the trajectory of the car);
- use non-hazardous infrared illumination rather than a flash to determine the license plate number.
Mobile tripods can be installed on road sections with high accident rates (more than 3 accidents over the last year), a high concentration of traffic violations or poor visibility, at intersections and near schools.
It is not allowed to install cameras on non-emergency sections of highways, in bushes, behind poles, behind road bends, in a car or behind a car body, on a highway with large elevation changes, on unlit sections of roads in the dark, or in the absence of a 3-meter wide shoulder. Each camera must be equipped with an infrared license plate recognizer, internal memory and photo printing options.
Grounds for canceling a fine from a camera
The claims of traffic police inspectors against the driver are not always justified. You can challenge the imposed fine in the following situations:
- the employee did not explain what violation was committed by the driver;
- the photograph does not show a sign, the rule of which the driver violated in the inspector’s opinion;
- the device was hidden by an employee;
- the inspector offers to delete data about the violation from the device’s memory for a “cash bonus”;
- The driver's video recorder readings differ from those of the inspector.
Note to motorists
In order not to get caught on one of the radars, it is advisable for drivers to adhere to simple rules:
- follow traffic rules no matter what road you are driving on;
- purchase your own DVR, which will allow you to defend your position if problems arise;
- do not respond to the inspector’s provocations if he begins to blackmail you and do not agree to a bribe. If you nevertheless violated traffic rules, then you need to pay a fine officially;
- use radar detectors. These devices allow you to monitor video cameras. Unfortunately, many modern cameras have learned to bypass these detectors.
The problem with video recording cameras is difficult to call solved. Drivers forced to defend their rights go to court and often lose. However, the development of GOST standards and the state’s attempts to combat the permissiveness of private owners and inspectors encourages people to believe in future changes.
How it works?
After the adoption of the bill, private video recording of traffic violations became possible and legal. At the same time, both sides remain in the black: budget funds are not spent, which makes it possible to find other options for financing, and entrepreneurs get the opportunity to earn money.
Previously, according to the same plan, private investors worked with video recording cameras on toll roads. Now it has appeared on public highways as well. The legality of the actions is confirmed by amendments to the law “On Concession Agreements”.
The businessman just has to install the camera and wait to make a profit. In this case, the funds are transferred first to the state treasury (after the violator pays the fine), and only then to the owner of the equipment. The money is not transferred in full. Some funds remain in the budget. The investor's remuneration can reach 233 rubles for each fine.