Oddly enough, the question of what is the difference between parking and stopping has been a significant problem for many years.
The distinction between these concepts has often put many motorists in a difficult position, even though they are described in detail in the traffic rules.
However, drivers often come into conflict with traffic police.
The problem exists and to solve it, every driver should clearly understand the difference between parking and stopping from the position of traffic rules.
In order to identify the differences between these concepts, you need to know what a stop is and what a parking is, the definition of each maneuver separately.
In simple terms, these terms differ in their duration. Stopping is a short maneuver. The parking lot is long. But there are other differences as well.
A stop is a deliberate cessation of movement of a vehicle for up to 5 minutes, but traffic rules allow for exceeding this period.
A prerequisite for a stop is the need to load or unload goods, or board and disembark passengers.
Parking is also a deliberate stop to the movement of vehicles, but for a period of more than 5 minutes for reasons not related to the conditions required for stopping.
If the stop lasted no more than 5 minutes, then such an action is considered a stop. In this case, it does not matter what the passengers and driver are doing at this time.
If traffic was stopped intentionally to board or disembark passengers, or to unload or load a vehicle, such a maneuver is considered a stop. In this case, the duration of the maneuver does not matter.
All other deliberate stoppages of movement lasting 5 minutes or more and not related to the mandatory condition of stopping are considered parking.
So the difference between parking and stopping is as follows:
- Parking implies a duration, and stopping is a short-term maneuver.
- Stopping is not always prohibited where parking is prohibited.
- Parking will always be a violation in places where stopping is prohibited.
To distinguish between these maneuvers, you need to understand the difference between the “No Stopping” and “No Parking” signs.
If there is a sign “Stopping is prohibited” - 3.27 (in the old version of the traffic rules 3.34), it is prohibited to stop and park.
This sign has the shape of a blue circle with two crossed red stripes.
And the sign “No parking” - 3.28, allows you to stop if necessary.
The sign is round in shape with one red stripe on a blue background.
Video: Stopping and parking
Chapter 12 of the traffic rules describes the rules for stopping and parking vehicles. In accordance with them, the vehicle can be parked in the following places:
- Stopping and parking of vehicles is allowed on the right side of the road on the side of the road.
- If it is absent - at the edge of the roadway.
- In certain cases established by traffic regulations - on the sidewalk.
First of all, the vehicle should be parked on the side of the road
. Other options are allowed only if it is not available.
It is important to take into account that if the side of the road is occupied by other cars or something else, then parking the car on the roadway is not allowed.
Parking vehicles on the roadway at its edge is only possible when there is no shoulder.
Quite often situations arise when a driver who does not know how to reverse park between cars parks his car a meter from the edge of the roadway. This is considered a traffic violation and should not be done.
You can stop on the left side of the road only in populated areas and only in the following cases:
- Two-lane roads with one side in each direction, but no tram tracks in the middle. If tram tracks are located on the right or left, this does not prohibit stopping on the left side of the road. But in such areas there is often a continuous marking line, which does not allow parking or stopping on the left side of the road.
- In one-way areas. In this case, the presence or absence of tram tracks does not play any role. But trucks may stop on the left side of one-way roads only to load or unload work. This means that in this situation the truck cannot park, stop for less than 5 minutes, or stop to pick up or unload passengers.
Chapter 12.2 of the Traffic Regulations describes how to park vehicles correctly.
Cars are allowed to be parked in one row parallel to the edge of the roadway and as close to this edge as possible.
Thus, if the driver does not know how to parallel park and tries to park in front at a small distance, then most likely he will park the car at an angle. Such an action is considered a traffic violation and is subject to a fine.
Two-wheeled vehicles without a side trailer can be parked in two rows
. This means that one of the motorcycles may not be parked at the edge of the roadway.
Parking cars at an angle to the roadway is permitted only where there is local widening of the roadway. In addition, road signs and markings must indicate this at the same time.
Parking on the edge of the sidewalk that borders the roadway is permitted only for passenger cars, motorcycles, mopeds, and bicycles in those places indicated by sign 6.4 along with one of the signs 8.4.7, 8.6.2, 8.6.3, 8.6.6 — 8.6.9.
These signs and plates mean the following:
- “Parking location” - 6.4.
- “Type of vehicle” - 8.4.1 - 8.4.8, indicate the type of vehicle to which the sign applies.
- “Method of parking cars” - 8.6.1 - 8.6.9.
It should be taken into account that only passenger cars, motorcycles, mopeds and bicycles have the right to park on the sidewalk. But it is no longer possible to place a cargo gazelle on the sidewalk.
In accordance with the rules, in the absence of a certain sign, stopping a passenger vehicle on the sidewalk will be considered a violation. And stopping a truck on the sidewalk - in any case.
For violation of stopping and parking rules in 2021, the law provides for penalties:
Every driver should know the concept of parking and stopping according to traffic rules, as well as the differences between them.
. Stopping is a short maneuver, and parking involves a long period of deliberate cessation of movement.
Parking does not oblige the driver to have specific reasons. A stop, as a rule, lasts no more than 5 minutes and has mandatory conditions.
Often, drivers violate traffic rules due to ignorance of the differences between parking and parking. This threatens with a fine, and with systematic warnings, even administrative liability is possible. This is especially true in some countries where the vehicle can only be parked in designated areas. Violation of the rules may lead to deportation followed by a ban on entry into that state.
Definition
Parking
is a place where any vehicle can be rendered inoperative and left for a short period of time. A special feature is the possibility of stopping the car for free.
Parking
is a place where a car owner can leave his vehicle for a long time and, for a fee, transfer responsibility for the safety of the car to a parking attendant. This concept also applies to garages and closed buildings.
Comparison of parking and parking
What is the difference between parking and parking? First of all, it's a fee. Parking most often does not require payment; it can be done near shops, hospitals and bus stops. But the car should not be stationary for a long time. As a rule, this concept refers to taxis, buses and minibuses. But an ordinary car can park near a certain place to drop off passengers. Parking, on the contrary, allows you to leave your car for a long time. For this purpose, there are special places near shopping centers, hospitals and public catering places. In this case, you also won’t have to pay for parking. But the car will not be guarded.
Another option for parking and parking is in a paid guarded area. The driver pays the dispatcher for a certain time for which he needs to leave the car. Only the territory is guarded in the parking lot, but the dispatcher will not be responsible for each vehicle. This also applies to property inside the car.
It's different in the parking lot. For a fee, the security guard takes responsibility for the safety of the car and the property inside it. In case of theft or theft of a car, the parking employee will be responsible. But this happens extremely rarely due to the closed territory and access system. And not everyone can afford expensive parking.
Another feature is that parking can only be done in strictly designated areas. Violation of this rule, that is, stopping a vehicle under a prohibiting sign, faces a hefty fine. Short-term parking does not require special spaces. If the engine is running and the driver is inside the car, then he is allowed to stop for a short time at almost any place.
Parking and parking difference
Owners of paid parking lots often refuse to bear responsibility for the safety of cars, citing the fact that they only provide parking services.
Kiev resident Alexander Bondar came to the resort for medical treatment, and instead of resting, he was forced to repair his foreign car: leaving his car in a paid parking lot near the sanatorium, he found it with a broken windshield. The owners of the guarded parking lot refused to pay for the installation of new glass, citing the fact that they only provide parking services, and therefore are not responsible for the safety of the car.
What is the difference between a parking lot and a parking lot and how can an owner obtain compensation for a damaged car? FACTS learned from experts.
“The head of the parking lot self-confidently declared: “You want to make money from us, but nothing will happen to you!”
“At the end of April, I came to Truskavets to relax, drink local healing water,” recalls Alexander Bondar . — Once upon a time, I had already been to this resort and lived in the Vesna sanatorium. Therefore, for old times’ sake, I decided to stop in the same place. In addition, a car could be parked next to the building. Since the foreign car is not mine - I drive by proxy, it was important that the parking lot was guarded, with surveillance cameras and equipped with a barrier. I paid 16 hryvnia for a day to use the parking lot and didn’t even attach much importance to the fact that the receipt said: “Payment for parking services.”
*Alexander Bondar: “I completely disagree with the court’s decision that responsibility for the broken glass rests solely with the owner of the damaged car. And he filed an appeal” (photo by Sergei Tushinsky, “FACTS”)
I didn’t really like the sanatorium, so I moved to another one and left my car in the same parking lot. A couple of days later I needed an umbrella that was in the car. When I arrived at the parking lot, I saw that the windshield of my Mitsubishi L 200 was broken. It seemed as if a stone had been thrown at him, because cracks appeared on the glass, spreading in different directions from one hole about two centimeters in diameter.
I called the security guard over and showed him the broken glass, but he said that he had nothing to do with this problem. I had to call his boss. The proceedings lasted for three hours, as a result of which they told me that... I myself broke the windshield of my car and decided to blame the guards for this in order to receive payment for replacing the glass.
The head of the parking lot self-confidently declared: “You want to make money from us, but nothing will happen to you!” Then he called someone in front of me, saying that he was a high-ranking official from the local police. Turning on the speakerphone, he pointedly put his mobile phone in my face, and I heard from the receiver: “Tell him that we are not responsible for anything, because this is a parking lot, not a parking lot!”
Then I decided to contact the administration of the sanatorium, but they told me: the director had left for Kyiv and would not return soon. However, even without the director, they once again made it clear: they are not going to pay for me to replace the glass. Like, the owner of Truskavetskurort, which includes the Vesna sanatorium, is a very influential person in the oil business, and such a small fry like me can’t achieve anything.
I had to call the police. Law enforcement officers drew up a report and opened criminal proceedings. While the proceedings were ongoing, the car remained in the same parking lot for 10 days, which I duly paid for.
The holiday was hopelessly ruined. I had to hire a lawyer and bring a specialist from the Lviv Scientific Research Institute of Forensic Expertise, since I was accused of breaking the glass myself, and from inside the car. Although the expert came to the conclusion: the blow to the windshield was made from the outside, most likely with a stone or brick. The examination cost me 1,476 hryvnia, plus glass replacement - 8,139 hryvnia. If the foreign car was mine, I would have bought cheaper glass, but the owner asked to supply “original” glass, so I had to contact the official Lviv dealer.
When I moved the car to another parking lot, its security guards, noticing that the car’s windshield was broken, entered this information into a special journal under my signature. There was nothing like this in the parking lot near the Vesna Hotel! This means that initially I drove into that ill-fated parking lot with a whole car!
“You can just as easily buy sausage in a store and receive a receipt in your hand stating that bread was purchased.”
In the end, the case went to court. Victoria Abakumova-Mudra, lawyer of Alexander Bondar , told FACTS that according to the law, parking lot employees are responsible for the safety of the car. If we are talking about parking, then the owner leaves the car there solely at his own peril and risk, paying only for a place on the asphalt.
— What is the difference between parking lots and parking lots?
— The parking lot is usually fenced and equipped with CCTV cameras and a barrier. Parking can be arranged in any part of the city, even on a small asphalt patch.
According to the rules for storing vehicles in parking lots, responsibility for the protection of cars and property located on the territory of the parking lot lies with its employees. In addition, they are obliged to provide services in compliance with the requirements of the Law of Ukraine “On Protection of Consumer Rights”.
And parking attendants do not bear any responsibility in the event of damage or theft of a car left in their care. But, before opening a parking lot, its owners are required to obtain permission from local authorities for its equipment, in addition, they must regularly pay taxes to the budget.
The difference between parking and parking is as follows:
- Parking is free for a short period of time.
- You can park near stops for disembarking passengers, and this is not considered a traffic violation.
- In long-term parking, the car is not guarded. No one is responsible for the safety of either the appearance of the car or the property inside.
- Parking is more expensive, but the car is completely safe there, including the property in the cabin.
- Parking may only be done in designated areas. Violation of this rule may result in a serious fine. People traveling abroad by car should pay attention to this.
- Parking can be in the form of a garage or an area under a canopy, which will protect the car from precipitation.
Parking and everything connected with it has long been on the minds of domestic car owners. This is explained primarily by the fact that this term means both a public facility intended to house a vehicle and an action associated with placing a vehicle in long-term storage. These topics become especially relevant for citizens living in small towns and entering the metropolis with their own car; this is where the greatest danger lies for them, receiving large fines.
What is the difference between a parking lot and a parking lot and how can the owner obtain compensation for damaged...
Owners of paid parking lots often refuse to bear responsibility for the safety of cars, citing the fact that they only provide parking services.
Kiev resident Alexander Bondar came to the resort for medical treatment, and instead of resting, he was forced to repair his foreign car: leaving his car in a paid parking lot near the sanatorium, he found it with a broken windshield. The owners of the guarded parking lot refused to pay for the installation of new glass, citing the fact that they only provide parking services, and therefore are not responsible for the safety of the car.
What is the difference between a parking lot and a parking lot and how can an owner obtain compensation for a damaged car? FACTS learned from experts.
Advice for consumers
- When leaving your car in the parking lot, check with the service personnel what status this piece of asphalt has.
- Always keep the receipt or other document issued by the parking attendant or security guard.
- If the car already has damage, then before accepting it for parking, a corresponding detailed entry is made in a special journal.
20776
Read us in the Telegram channel, and
Source: https://fakty.ua/190915-chem-otlichaetsya-avtostoyanka-ot-parkovki-i-kak-vladelcu-dobitsya-kompensacii-za-povrezhdennuyu-mashinu
What is this
If you adhere to the legal characteristics of this term, then you can find its wording in several official documents at once:
- Dictionary of financial and legal terms, paragraph 21.
All standards have the same meaning for this term, the only differences are that it is presented in different words. From them the following follows: parking is a specially marked area related to a highway, adjacent land or other areas intended for organizing parking of cars and any other wheeled vehicles on a paid or free basis. The conditions of accommodation, payment and operating hours are established by the owner of the land plot, the corresponding building or its separate part.
What is taken into account when constructing a parking lot?
Modern parking lots are quite complex structures, the construction of which requires careful preliminary preparation. Initially, a construction project is developed. This is a complex and time-consuming process comparable to the development of building construction projects or engineering structures. Various factors, both technical and legal, are taken into account. Only professionals can do this kind of work.
The set of necessary documents is similar to that collected before the construction of residential buildings. As practice shows, the quick payback of parking complexes makes them an attractive investment opportunity.
The project documents indicate the maximum parking capacity, area and expected income level.
Multi-level parking lots are serious capital-type structures. They have a wide driveway, a façade, and designated parking spaces. The parking lots are equipped with ventilation, video surveillance, a fire safety system, alarm system, lighting system and other amenities. All this attracts a larger number of customers and distinguishes parking lots from ordinary parking lots, including paid ones.
When organizing parking, be sure to take into account the following customer requirements:
- 24-hour security system for cars and people.
- Lighting and quality of flooring.
- Availability of entry and exit passages.
- Sufficient parking space in the parking lot, i.e. sufficient area allocated for the car.
For such parking lots there are additional requirements:
- Availability of heating system and climate control.
- Installation of ventilation, waterproofing, environmental control.
- Ensuring uninterrupted operation of mobile communications.
- Providing better visibility, which is achieved by higher ceiling heights, high-quality lighting, wider entry and exit zones, and individual design solutions.
Most often, underground parking lots have no more than three levels, since a larger number is considered economically unfeasible and may be limited by local legislation.
Is this a roadway or not?
In refutation of the above, from the point of view of traffic regulations, parking can be called any place where it is not prohibited. This conclusion suggests itself if you think about it logically, which is quite often practiced in Russian laws. For example:
- if a car is parked on a lawn near a store, this is a violation, since driving on them is prohibited (in relation to Moscow this will be “Placement of vehicles in areas occupied by green spaces”, in other regions of the country other legal acts apply);
- the opposite situation applies when the car is placed in a pocket that does not interfere with the movement of pedestrians and other cars; there are no prohibiting signs nearby either. In this case, this area can be considered a parking lot.
The wording of the term clearly states that parking, depending on the situation, may refer to the roadway or not. For example, if it is located on the road, in the far right lane. Another option is when the parking space is made in the form of a parking pocket, in which case this element is considered a local extension, and therefore also belongs to it. A separate designated area intended for parking vehicles is regarded as an adjacent territory. Similar conditions apply to residential areas; in this case, the official requirements for parking and stopping cars are completely different.
Planning solutions for parking lots
Car parking lots are divided into four types, depending on the length of time the cars are stored:
- – permanent storage – more than a day (as a rule, they are placed outside the street);
- – long storage duration – 8 hours or more (at sites in front of enterprises and institutions);
- – average storage duration – 2–4 hours (for spectacular buildings and structures);
- – short storage duration – up to 2 hours (near shops, train stations, etc.).
In most cases, parking lots of the first two types are special areas located outside the street. Medium- and short-term parking can be located within the street area. This is convenient for motorists, since in this case they leave their cars at the least distance from the sites they visit.
The concept of “cell for placing a car” was introduced. Its dimensions should be 0.5 m larger than the dimensions of the car on all sides in order to be able to walk around the car on all sides (Fig. 4.11).
Rice. 4.11.
Car storage box:
D – length, m; W – width, m
Car parking within the street is located as follows.
1. On narrow streets, short-term parking lots for cars are located on the roadway or on the sidewalk (lawn) according to one of the schemes shown in Fig. 4.12.
It is possible to drive the car onto the sidewalk (lawn).
Rice. 4.12.
Placement of car parking along the sidewalk or lawn (dimensions in m):
A
– on the carriageway along the axis of the road;
b
– on the roadway perpendicular to the axis of the road;
c – on the roadway at an angle to the road axis; d
– with the outer wheels driving onto the sidewalk or lawn;
d – with
the entire body driving onto the sidewalk or lawn, except for the inner wheels;
e
– with the entire body driving onto the sidewalk or lawn
2. On the main driveways on a special stopping strip adjacent to the lawn, 3.0 m wide for short-term parking of cars and 3.5 m wide for parking of trucks (Fig. 4.13).
Rice. 4.13.
Placement of parking along the sidewalk or lawn on the roadway (dimensions in m):
- 1 – side stone; 2
– cell for storing a car in parking lots - 3. In lawns or on local driveways, if their width is more than 5–6 m, according to one of the following schemes (Fig. 4.14).
Rice. 4.14.
Parking lot layout:
A
– on the main passage along the side stone;
b
– on the main driveway with access to the sidewalk (lawn);
c
– in the lawns on a local thoroughfare
What do the signs mean?
Regulation of the place, method and conditions of parking means road signs and information plates:
- Sign 6.4 – indicating parking. Can be installed with additional signs indicating the distance to the object, direction of movement or other conditions.
- 8.1.1, 8.1.3 and 8.1.4 - information signs indicating the distance to the parking lot.
- 8.4.9, 8.4.10, 8.4.11. 8.4.12, 8.4.13, 8.4.14, 8.4.15 – characterizes the type of vehicle (buses, taxis, trucks, motorcycles, cars) to which this sign installed nearby does not apply.
- Signs showing the method of parking the vehicle.
- Plate 8.7 indicating that parking in the parking lot is permitted only for vehicles with the engine not running.
- Tablet 8.8 with the numbers 10, 15,20 means that you will have to pay a certain amount to park the car here. The exception is some categories of citizens who have benefit status. For example, for large families in Moscow in accordance with, edited on December 19, 2017, clause 6.39.
- 8.9 – maximum parking time.
- 8.17 – the sign is valid only for cars or motorcycles with.
- 8.24, warning drivers that a tow truck is operating in this area.
Recently, plate 8.17 has become the most formidable of all those presented above. The fine for parking under a prohibiting sign is 5,000 rub.(if there is no “Disabled” sticker on the car and there are documents confirming permission to use it).
Parking requirements
Depending on the type of parking, the requirements for it may differ significantly. For example, certain standards apply to an indoor multi-level building, while others apply to an open multi-level building located on a fenced plot of land. If in relation to the first case numerous conditions presented in the entire list of SNiPs and GOSTs will be applicable, then for the second this list is much shorter. As an example, below are several documents required for parking of any type:
The following list, presented in the table, addresses the specifics of compliance with the requirements of regulatory documents for complex architectural parking.
Table 1. Parking requirements.
| Document type | Number | Name, description |
| SNiP | 41-01-2003 | Heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems |
| SNiP | 31-05-2003 | Requirements for public buildings and structures |
| SanPiN | 2.2.1/2.1.11200-03 | Sanitary protection zone and classification of objects and structures |
| JV | 59.13330.2012 | Accessibility for people with limited mobility |
| JV | 104.1333.2012 | Engineering conditions to ensure minimization of flooding |
| NPB | 104-95 | Development of fire warning systems |
| GOST | 12.1.005-88 | Sanitary and hygienic requirements for air composition |
| GN | 2.2.4/2.1.8.562-96 (Ministry of Health of Russia) | Permissible noise level for public and residential premises |
| ONTP | 01-91(Rosavtotrans) | General standards for the design of enterprises related to road transport |
Based on the table presented, it becomes clear that the official opening of the parking lot currently occurs with the passage of numerous authorities and obtaining permission from them. The above list is not final; the specified standards were selected at random.
All types of parking
With the increase in the number of cars on the roads of our cities, the demand for parking spaces increases. Parking for the first time in large cities is becoming more and more difficult every day. This explains the increase in the number of paid parking lots using innovative technical solutions. The reason for the increase in the amount of fines for this traffic violation becomes obvious - modern drivers “throw their cars anywhere,” blocking the opportunity for other participants to continue driving. Of all the existing types of parking, several that are more popular can be noted separately:
Street flat, open, that is, without a roof.
Any of the presented options can be paid, guarded or free, created to relieve congestion on city roads. But in any case, each parking lot must be equipped with special preferential spaces intended for parking vehicles. Disabled people can move on them (either independently or with the help of third parties). This condition is stated in as amended on December 29, 2015. In addition, areas in front of small shops intended for visitors, as well as a place near the house: the area in front of the entrance, outside the yard or in an alley located nearby, can also be called parking lots.
Types of car parking according to purpose.
Characteristics associated with the specialized use of cars for which this or that type of parking is intended, according to the Rules of the RF DD, are indicated by road sign 6.4 (given above) with information signs or markings installed with it. To visually familiarize yourself with these types, the following pictures are given:
- Parking space for fire fighting equipment, designated in the courtyards of apartment buildings, established in accordance with » clause 75.
- or vehicles equipped with a similar plate. May be marked with markings or plate 8.17.
- In addition to the parking lots presented, parking of certain categories of vehicles is prohibited in the area covered by the sign, which does not allow them to travel in this area. For example, a truck cannot be parked in an area where it is prohibited from entering.
Illegal blocking of a parking space is quite popular in Russia. To a greater extent, such areas are monitored using video surveillance systems, and immediately after the vehicle begins to park, a person approaches it inquiring about the purpose of its arrival. From the point of view of the law, they cannot do anything, so any car owner has the right to park their car here. However, by doing the same, there is a possibility of finding a car in the parking lot hit by a sharp object, leaving a deep mark on the paintwork.
Parking methods
These conditions are regulated by installed information signs 8.6.1 – 8.6.9 or a certain type of road marking:
Parking at an angle of 45⁰.
- For Moscow and St. Petersburg, the fine can reach 3,000 rubles
.
In other constituent entities of the Russian Federation, for this violation of traffic rules, a penalty equal to 2,000 rubles
.
This condition is provided for in accordance with clause 4. Literally it looks like this: “Stopping and parking a vehicle is prohibited in places where the car will become an obstacle for other road users, block the visibility of regulatory traffic lights, signs...”.
Traffic police officers regard such an action as a violation of clause 4 “Violation of stopping and parking rules.” A similar situation applies to parking within the semicircular markings in a paid parking lot - the fine is identical. The top view of the presented photo shows that in this situation, car No. 1 is a traffic violation violator, as it is installed on a rounded marking.
Reverse parking algorithm
When you drive forward, you deprive yourself of free maneuvering when leaving. Therefore, it is better to park the car in reverse to the curb, and with the front towards the roadway.
You need to drive forward and place the rear of the car at the level of the first limit (1).
From reverse, we back up and turn the car so that the rear part rests against the corner of another restriction (2).
They stepped forward. And as soon as you see parking in the rear-view mirrors, we begin to refuel the car back.
The picture in the mirrors must continue. At the same time, we direct the center of the car to the middle of the width of the parking lot.
Traditionally, we call parking for cars the word “parking” or “parking lot”. But what is parking? Parking refers to large engineering structures, both underground and above ground, often multi-level, which are designed for temporary storage of cars. Thus, “parking” is a modern type of parking lot.
Types of illegal parking
When considering the option of illegal parking, you should refer to the traffic rules, here you can emphasize official and reliable information from the point of view of the law. A whole chapter No. 12 is devoted to listing how and where a car should be installed according to the rules. From it you can make a list of places where a ban on parking cars applies. Table 2. The most common types of illegal parking.
| Parking type | Amount of fine, rub. | Note |
| In places designated for parking for disabled people | 5 000 | Possible evacuation |
| At the bus stop | 1 000 | When obstructing the movement of public transport 2,000, according to clause 4 of Article 12.19 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation |
| On the zebra crossing | 1 000 | If a vehicle is found in a restricted area without a driver, it may be towed. |
| In the coverage area of signs 3.27 and 3.28 (Stopping and parking is prohibited) | 500 | According to . |
| In case of non-payment of paid parking | From 1,000 to 2,000 | On average, the driver is given 10–20 minutes to find a parking meter and deposit money. |
| In the courtyard | 1 500 | The courtyard area belongs to the residential area, in accordance with. "Movement in courtyard areas." The car owner is punished in the above-mentioned manner; in addition, a vehicle that interferes with the passage of special vehicles may be evacuated. |
| On Pavement | 1 000 | According to Part 3 of Article 12.19 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation “Violation of the rules for stopping and parking a vehicle.” |
Note!
The amount of fines for Moscow and St. Petersburg under some articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation may differ significantly. The presented list is not complete; more detailed information can be found on the official website of the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate of the Russian Federation gibdd. An exception may be parking with a driveway onto a lawn; in this case (as mentioned earlier), control is carried out by local authorities.
In addition, Russian legislation provides for penalties related to, prescribed in the Water Code, Part 4 of Art. 65 “Water protection zones and coastal protective strips.”
According to this document, for violating established boundaries, beyond which the violator is not allowed, is punished in accordance with “Violation of a special regime, carrying out economic or other activities on the coastal territory...”. Based on this, for driving to the shore of a river or sea, a vehicle may be subject to a fine ranging from 3,000 to 5,000 rubles
. At the same time, each natural object has its own distances, for example, to a river or lake it is 10 m, and for the sea or Lake Baikal it is 500 m.
Complaint about illegal parking
Before you complain about a neighbor who does not want to “wedge” his car between two cars standing next to him, but abandons it on the playground as shown in the photo, you need to have a photo or video recording of the incident.
The need for temporary parking
. This need exists in cities and on highways. It is especially large in administrative centers, areas of shopping, cultural and educational institutions, as well as near transport hubs and large residential buildings. On highways there is a need for temporary parking, independent of the location of the listed objects of gravity, but associated with the need for drivers to rest, inspect vehicles, etc.
Classification of temporary parking
. Temporary parking in cities is divided into street parking, i.e., when parking is allowed directly on the roadway, and off-street parking, i.e., remote from the roadway. Street parking is sometimes also called near-sidewalk parking, since standing cars, according to the Traffic Rules, should generally be located directly next to the sidewalk curb (in certain cases, it is allowed to place cars along the edge of the sidewalk). The method of parking cars in parking lots can be determined by marking lines and additional plates 7.6.1–7.6.9 to sign 5.15.
Off-street parking can be arranged in open areas, on the roofs of buildings, in special one- or multi-story parking garages. They construct above-ground and underground parking garages. Multi-storey parking garages, depending on the method of moving cars in them, are divided into ramp and mechanized. In ramp garages, cars move under their own power, while in mechanized garages, they move with the help of special elevators or conveyors. The need for multi-storey parking garages arises, first of all, in those places where it is impossible to allocate sufficient space for the construction of a parking lot, which is typical for the central business districts of large cities.
Foreign data show that in large cities with a high level of motorization, the overwhelming number of temporary parking spaces are provided through off-street parking. All temporary parking can be paid or free. Charging a fee, usually based on the length of time a vehicle is parked, not only recovers construction and operating costs, but has also been shown to improve the use of parking by vehicle owners. In this regard, parking lots have become widespread in the most cramped central blocks of many foreign cities, in which each space is equipped with a special parking meter for individual or collective use.
Temporary parking near highways is usually organized in open areas, since under these conditions there is usually no need to place a large number of cars in one place. At the same time, it is important to ensure sufficient frequency of parking spots.
Parking lots are divided according to operating mode: 1 – with unlimited operating hours; 2 – with a limitation on the length of stay of the car; 3 – with limited (during the day) operating time. Parking lots of the 2nd type are used in heavily trafficked areas and cramped conditions, which makes it possible to serve a larger number of car owners with a limited number of spaces. A typical example is the introduction in a number of Western countries of the so-called “blue zone” for street parking in a certain part of the city. The length of stay in a parking lot in this zone should not exceed 1.5 hours. This practically eliminates the possibility of using street parking in these zones by people coming to work, i.e., it excludes work trips, which lead to the longest stay of cars in temporary parking lots. To control the duration of parking in areas with limited time spent in a car, a cardboard dial with movable arrows is installed, on which the owner must indicate the time of arrival.
Type 3 parking regime is introduced on certain streets, the capacity of which at peak times is insufficient in the presence of parked cars. It can also be introduced at certain hours due to the need to perform special loading and unloading operations, cleaning streets or parking areas themselves. The same regime can be applied to off-street parking areas (for example, located near administrative and cultural centers) to prevent their transformation into a place for permanent storage of personal cars. A diagram showing the main classification characteristics of temporary parking lots intended for parking cars is shown in Fig. 9.8
Determining the size of parking lots
. When determining the required area for parking, one should proceed from the level of motorization in the region, the predominant type of cars for which it is calculated, the power of the serviced object of attraction and the expected average length of stay of cars in the parking lot during periods of intense demand. The area of one place is usually 20–25 m2 for passenger cars and 40–85 m2 for trucks and buses.
The length of stay of passenger cars depends primarily on the nature of the facility being serviced and the purpose of the trip. The following typical purposes of travel can be named: to work (study); official and business (during working hours); cultural and everyday, excursion and tourist, etc. The shortest duration of one-time parking is observed during official and business trips and visits to trade and household enterprises. The duration of a car's stay in such parking lots does not exceed 1 - 1.5 hours. The time spent in the parking lot of entertainment enterprises is determined by the duration of the performance. The longest time cars spend in parking lots when commuting to work is determined by the length of the working day. Research shows that the length of time a car stays in almost all types of parking lots is significantly influenced by the size of the city. In the largest cities, compared to small cities, parking time approximately doubles.
SNiP 2.07.01–89* contains standards that are intended for urban planning and can be used to justify operational measures for organizing temporary parking. The standards are designed for a level of motorization of up to 250 cars/1000 people, and for higher values they should be increased.
Separate areas or near sidewalk areas should be allocated for taxi cars in places where there are capacity reserves.
Parking is a painful topic for residents of large cities, especially capital cities: Moscow, Kyiv, St. Petersburg. In this article, we’ll try to understand the parking rules so that one day you don’t have the chance to see your car being taken away on a tow truck.
These issues are described in detail in section 12 of the Road Traffic Rules.
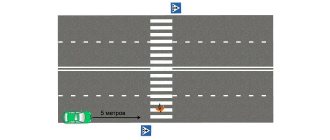
Leaving a car for longer than five minutes is permitted:
- no closer than 5 meters from a zebra crossing or intersection;
- 15 meters, but not closer, from bus stops;
- 50 meters from railway crossings.
This section of the traffic rules also lists various road signs in the coverage area of which parking and stopping are permitted. Thus, in tight city streets, cars can be parked parallel to the sidewalk. Sometimes a sign 8.6.1-8.6.9 is posted under sign 6.4, it shows exactly how you can park a car in a given place - parallel or perpendicular to the curb, on the sidewalk, and so on.
By default, if there are no prohibiting signs, solid, intermittent (zigzag) yellow markings, park the car:
- parallel to the edge of the roadway;
- on the right edge (if the road is one-way, then on the left is also allowed);
- on the side of the road.
If you are on a long journey and have to spend the night on the way, then you need to look for service signs on the highway - Camping, Rest Place.
Stopping on the side of the road for long-term parking, especially in the dark, is prohibited.
Parking, parking, parking – is there a difference?
Parking is a concept that has taken root in speech relatively recently. In fact, there is no difference between parking, parking and parking. However, we are accustomed to perceive these words differently.
What do you think of when you hear “parking lot”? Most likely, an open-air area with or without perimeter fencing. Parking is already commonly associated with neatly lined spaces near shops, restaurants and office buildings.
When the first covered multi-level parking lots began to appear, the word “parking” came into use. Parking has begun to be perceived as a modern way of storing cars, which is more complex than a regular parking lot. A separate building where cars are stored? - Parking. Underground two-level parking? No, “underground two-level parking” sounds better. What do you call the area on the roof of a hypermarket building where parking is organized? And again parking.
You may or may not agree with this division. But it has taken root at the level of perception, and it is convenient. There is no clear and strict definition of what parking is, but technically, parking, like a parking lot, and a parking lot are specially organized parking spaces for cars.
Where can you park your car?
Paragraph 12.4 of the traffic rules is entirely devoted to this problem. The most basic rule is that you don’t need to park, or even stop at all, where it will create obstacles for other drivers of pedestrians, trams and trolleybuses.
Let's list the main places:
- tram tracks, railway crossings, overpasses, tunnels, bridges - in a word, all those engineering structures where there is active traffic, or car routes intersect with the routes of other modes of transport;
- on those sections of the road where the distance from the edge of the sidewalk (curb) to the dividing line is less than three meters;
- on and before crossings, intersections;
- at sections of the route with limited (less than 100 m) visibility, before or behind dangerous turns;
- in the area where minibuses, trams, etc. stop.
Please note that all of the above applies to both stopping and parking.
You also need to pay attention to various road signs: parking/stopping is prohibited (for example, on even/odd days). You cannot park your car in spaces reserved for disabled people or marked with special signs.
Among other things, you need to avoid parking where your car will block the view of drivers of other vehicles.
About parking in yards
There are special rules that apply here, which we previously discussed.
Let's recall them again:
- the distance from the parked car to the wall of the building is at least ten meters;
- It is prohibited to park on lawns and playgrounds;
- if the parking area is designed for up to 50 vehicles, it can be open, but if there are more than 50, it must be separated by a fence;
- Trucks weighing more than three and a half tons cannot be parked.
It must be remembered that in adjacent areas - in the courtyards of residential buildings - priority belongs to pedestrians.
Regulatory requirements for parking space size
It is recommended to place parking spaces for people with disabilities close to the entrance to the parking lot; on the one hand, this will save space, and on the other hand, it will allow people with disabilities to park closer to the exit for ease of movement.
Typically, parking spaces for the disabled are located within fifty meters of institutions (clinics, social services and other institutions where there is a high likelihood of persons with disabilities).
Such places are marked with special road signs; usually 10-20% of all parking spaces are allocated for them. The width of a parking space for disabled people must be at least three and a half meters for the convenience of passengers and drivers.
For trucks
The practice of organizing parking lots and parking lots shows that it is not practical to allocate space for heavy trucks in the parking lot of passenger cars. Photo 5. Example of truck parking location:
Typically, separate parking lots are equipped for them, taking into account the following conditions:
- the possibility of through passage through the entire parking lot must be created;
- the arrangement of distances between rows should be as wide as possible so that nothing prevents heavy and bulky cars from turning into or out of a parking space.
It is necessary to apply markings that allow reversing;
Basic rules and types of markup
Among the basic rules for applying markings in parking lots, the following should be highlighted:
- Be sure to take into account the dimensions of vehicles of any brand.
- A person must move freely between two cars from adjacent rows standing with open doors.
- It is necessary to keep in mind that not all drivers are experts in their field, there are many newcomers behind the wheel, not everyone knows how to park correctly, so when applying markings you need to take this factor into account as well as the need to maneuver when entering and leaving the parking lot.
In addition to the basic rules, there are also so-called minor ones, which also need to be taken into account when arranging parking:
- The thickness of the marking lines should be clearly visible both during the day and at night; in recent years, more and more parking lots have been marked with paint with a reflective effect.
- Fences, bollards, columns and other elements must not interfere with vehicles and in no case should they reduce the minimum size of a parking space.
- The markings must be applied in strict accordance with the standards.
According to GOST standards, the following requirements must be met:
- the width of the passage between rows of parking spaces must be at least six meters;
- deviation from standard marking lines should not be more than five centimeters;
- when updating marking lines, old, half-erased lines must either be deleted, or new lines must be drawn strictly along the old ones, so that some do not duplicate others;
- markings should be applied only in the warm season in dry weather;
- The width of the marking lines should not be thicker than ten centimeters;
- Marking lines must be updated every six months; if this is not possible, it is better to use cold plastic to apply markings.