Railroad crossings
According to clause 15.1 of the traffic rules, crossing railway tracks is possible only at railway crossings.
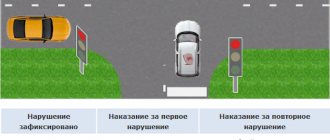
Anyone who tries to drive in the wrong places is either subject to an administrative fine or deprived of their license for up to 6 months. Railroad crossings are divided into two types:
1. Adjustable railway crossing - a type in which one or more warning structures are installed at the crossing:
- traffic light
- sound alarm
- barrier
- metal shield blocking the path
- duty booth
2. Unregulated railway crossing - a type that does not have any of the above warning methods.
Railway Telegraph
01/09/2021 at 14:00 48 min. at the station Daban V-SIB, when performing shunting movements at a speed of 19 km/h, was allowed to pass the traffic light N1 with a prohibiting indication by locomotive 3ES5K N 456 TCHE Vikhorevka V-SIB T under the control of the TCHM, operating without TCPM, with subsequent cutting of switch N 6. The investigation established that that at 14 o'clock. 32 min. after the arrival of freight train No. 2448, the pushing locomotive 3ES5K N 456 was uncoupled from the tail of the train. At 14:00. 37 min. The control cabin was changed and, in violation of the requirements of paragraph 18 of the Procedure for the use of safety devices, approved by the order of JSC Russian Railways dated 02/04/2019 No. 183r (Procedure), the procedure for switching from the “Train” mode to the “Shunting” mode was violated to turn on the “white” light" at the locomotive traffic light on a coded section of the track. At 2 p.m. 47 min. after receiving a command from the DSP to follow the shunting order from the traffic light “Ch1” from the 1st track to the 2nd occupied track, leaving behind the shunting signal of the traffic light “M1”, the TCM set the locomotive in motion in the opposite direction. At 2:48 p.m. TChM at a speed of 19 km/h on the white light of the locomotive traffic light allowed the passage of the traffic light “H1” with a prohibitory indication, followed by the cutting of switch No. 6, and was stopped by the auxiliary brake at the command of the chipboard after 86 meters. When listening to the negotiation registrar, it was established that the TCH and DSP were violated by the Basic Rules of Negotiation, set out in paragraph 1.3. The general provisions of the Recommendations for the application of Appendix No. 20 to the IDP, approved by the order of JSC Russian Railways dated July 4, 2017 N 1258r, namely, the negotiations were not conducted briefly and clearly. After arriving with the train at the station, before directly receiving the shunting work plan, a dialogue took place for a long time between the DSP and the TCM “which side is better to carry out the shunting movements.” As a result, the final information of the shunting movement plan was not correctly perceived by TCH. The reasons for passing a traffic light with a prohibiting indication were to set the locomotive in motion in the opposite direction and failure to observe the traffic light indication. In 2021, TBI was included in the risk group three times according to the following criteria: results of decoding storage media - twice in February and July 2021 and over-consumption of fuel and energy resources in July 2021. When checking the quality of decoding storage media, it was revealed that violations of the Procedure for transition from The “train” mode for “Shunting” at TCHM was allowed on 01/01/2021 and 01/05/2021. The storage media are sent for repeated decryption. Similar violations of the Procedure were committed by other TBIs. During the investigation of this case, it was also established that there was no check and control of the performance of the wearable part of the TSCBM by the TChD using the PNC remote control when the TChM reported to work.
Passage of controlled railway crossings with barriers
Any controlled crossing over railway tracks is indicated by different road signs depending on whether it has a barrier or not and how far away it is.
Approaching a railway crossing:
- The first sign is installed 150-300 meters from the crossing. At this distance, overtaking is only allowed for cars moving at low speeds.
- The second sign is installed at a distance of 100-200 meters from the danger zone. Overtaking is prohibited from this distance.
- The third sign indicating the approach to the railway crossing is located 50-100 meters from the crossing. In addition to the ban on overtaking, there is a ban on parking of vehicles.
Signs and approach distances to railway crossings.
When crossing a railway crossing is prohibited
According to clause 15.3 of the traffic rules, crossing the railway track is prohibited when:
- train approaching
- closed barrier
- red traffic light
- prohibiting signal from the duty officer
- traffic jam behind the crossing
Any of these conditions is sufficient to stop the vehicle. In this case, the driver must stop either at the STOP sign or near the stop line. If they are missing, then you need to leave 5 meters to the barrier.
If it is absent, the distance to the nearest edge of the rails must be at least 10 meters. It is better to drive through a railway crossing at the highest possible speed, but taking into account the unevenness of the road, in order to leave the danger zone as soon as possible. Railroad crossing rules do not recommend driving onto the tracks until the previous vehicle has left the crossing. This is necessary so that in case of an unforeseen situation you do not have to stop on the railway tracks, thereby further aggravating the situation.
In the event of a malfunction of a barrier, traffic light or alarm system, the duty officer is obliged to independently regulate the movement of vehicles using his hands or red flags.
New fine for ignoring an approaching train
Let's look at Part 1 of Article 12.10 of the Code of Administrative Offences:
Article 12.10. Violation of the rules of movement across railway tracks 1. Crossing a railway track outside a railway crossing, entering a railway crossing when the barrier is closed or closing, or when there is a prohibitory signal from the traffic light or the person on duty at the crossing, as well as stopping or parking at a railway crossing -
shall entail the imposition of an administrative fine in the amount of one thousand rubles or deprivation of the right to drive vehicles for a period of three to six months.
1. Crossing a railway track outside a railway crossing, entering a railway crossing with a closed or closing barrier or when there is a prohibiting signal from a traffic light or a crossing officer on duty, stopping or parking at a railway crossing or driving through an unregulated railway crossing if a train (locomotive, trolley), -
shall entail the imposition of an administrative fine in the amount of five thousand rubles or deprivation of the right to drive vehicles for a period of three to six months.
Two important changes have been made to this part:
1. A new violation has been added, namely that the driver at an unregulated crossing ignored the approaching train and continued driving through the crossing.
Until May 1, 2021, this violation fell under Part 2 of Article 12.10 of the Code of Administrative Offenses and could only result in a fine. Starting from May 1, an additional punishment option will be introduced in the form of deprivation of rights for a period of three to six months.
2. The amount of the fine under Part 1 of Article 12.10 has been increased to 5,000 rubles .
Passage of unregulated railway crossings
What signs are installed before a railway crossing?
Unequipped crossings are found in areas remote from populated areas. Often at such crossings there is a sign requiring people to stop before crossing the tracks. All rules for calculating distances coincide with those indicated when crossing a controlled crossing. After braking, you need to make sure that there is no train. This can be done visually, but if there are descents, ascents and turns, it is better to get out of the car and check the approach of the train by ear. It is better to do the same at night and during increased fog. After this, you can continue driving and cross the crossing.
Sign 2.5 “Moving without stopping is prohibited” in front of the railway crossing
The topic of today's discussion is the passage of railway crossings.
Question: If a white-moon traffic light is on at a railway crossing and a STOP sign is installed - “Moving without stopping is prohibited,” then what should you follow? When driving through a railway crossing, do you need to stop at the sign?
Answer.
The red octagonal sign with the inscription STOP – sign 2.5 “Moving without stopping is prohibited” belongs to the group of priority signs. In accordance with paragraph 6.15 of the traffic rules, a working traffic light cancels the effect of priority signs. When the traffic light is not working (turned off), the driver must follow the priority signs, in your case the requirement of sign 2.5.
According to GOST R 52289-2019, sign 2.5 should not be installed at railway crossings equipped with traffic lights. Below is an excerpt from the document.
"5.3.7. ... The sign is installed in front of railway crossings (without an attendant, not equipped with traffic lights) together with sign 6.16, at a distance of 10 m to the nearest rail in cases where, at a distance of 50 m from the nearest rail, the visibility distance of the train is less than the value specified in table 6" (table can be found in GOST R 52289-2019).
Despite these rules, the mentioned combination of sign 2.5 and traffic light occurs, for example, this is evidenced by the picture below (the picture is real). Perhaps the traffic light in this case is not working properly, perhaps they did not dismantle it, but installed sign 2.5 “No stopping without stopping”, the reason is not important. There is a fact - the presence of both a railway traffic light and a 2.5 sign.
A traffic light with a white-moon signal is a full-fledged traffic light (clause 6.1 of the traffic rules), which regulates the movement of vehicles across railway tracks.
When the traffic light in front of the railway crossing is working (the white-moon signal is flashing - movement across the tracks is allowed), then there is no need to stop.
If the traffic light in front of the railway crossing is not working (not a single signal is on), then before continuing to move, you should first stop at sign 2.5. A stop is required!
Paragraph 15.2 of the traffic rules: “When approaching a railway crossing, the driver must be guided by the requirements of road signs, traffic lights, markings, the position of the barrier... and so on.” In your case, one of the above is either a working traffic light or a priority sign 2.5 “Driving without stopping is prohibited.” The traffic light does not work - sign 2.5 comes into effect.
Where do you need to stop at a prohibitory signal (traffic light or the duty officer at the railway crossing)?
When driving through the railway tracks is prohibited, the place to stop the car is regulated by clause 15.4 of the traffic rules: “... at the stop line, sign 2.5 or traffic light, if there are none - no closer than 5 m from the barrier, and in the absence of a barrier - no closer than 10 m to the nearest rail."
You should pay attention to the sequence in which the stop locations for the prohibitory signal are listed, i.e. what you need to pay attention to first. The very first thing is the presence of a “stop line” (marking 1.12 or sign 6.16 “Stop”). If there is no “stop line”, then you need to stop at sign 2.5 or a traffic light, etc.
Of course, no one will control the exact footage to the rail or barrier, but the main thing, after all, is a safety issue.
Rules for moving a railway crossing when you have to stop at it
If you are forced to stop at a railroad crossing and the vehicle stalls while crossing the railroad tracks, it is necessary to remove it from the rails as soon as possible. But before this, the emergency alarm must be turned on, and all passengers, if any, must be disembarked and taken out of the danger zone. Then you need to contact the attendant and have the vehicle towed with the help of other motorists.
There are situations when the car is the only one on the road, and you can’t start it with the handbrake. Then it is necessary to send two assistants to different directions of the railway tracks at a distance of about a kilometer in order to signal the driver about the incident. They represent circular movements of the hands with a red flag or any other red material. At night, a lantern is used instead of a cloth. If there are no assistants, you should use Morse code and start broadcasting the letter “B”. It consists of one long and three short beeps and means trouble.
When crossing railway crossings, you should always remember the full extent of the possible injury hazard of this event. A train weighs many times more than a car; a braking distance of several meters is clearly not enough for it. Although the legislation of our country is doing its best to reduce the number of accidents in any situation, personal care and responsibility have never failed anyone.
Video: Rules for driving through a railway crossing.
What types of traffic lights are there on the railway?
Hello everybody!
A small topic: what types of traffic lights are there on the railway?
Dwarf traffic light
This is a very serious topic, because traffic light signals are the most basic thing on which train movement is based; locomotive crews are obliged to unquestioningly fulfill, so to speak, the requirements of the signals. In fact, there are a lot of them and each signal carries information that is perceived by the driver and the train’s mode of movement directly depends on the readings of the traffic lights! All operation of traffic lights and their signals are strictly regulated in the “Instructions for Signaling on Railway Transport of the Russian Federation” and not a step aside!
Mast traffic light
Traffic lights are classified according to their design: mast and dwarf. Mast-mounted – traffic lights, the signal blocks of which are installed on high mast supports. Dwarf traffic lights, the signal blocks of which are installed on small foundations, usually no higher than average human height, and are installed mainly at stations.
But here, according to the nature of their, so to speak, direct responsibilities, traffic lights are divided into: entrance and exit - installed in the necks of stations, at the entrance and exit;
route traffic lights - are installed at stations, because stations are very large, marshalling and consist of many areas, so-called “parks”, so route traffic lights are installed to travel from one station area to another;
checkpoints - traffic lights are installed on stretches, limiting block sections;
repeating ones - are installed, as a rule, at stations where the visibility of the entrance, exit or route traffic lights is difficult, for example in a curve, so the repeating traffic light duplicates the indication of the main one;
barrier ones - usually installed in front of railway crossings, in the normal position they do not light up any signal, but if an obstacle arises at the crossing and the train is already close, a red light lights up at the barrier traffic light and the driver can apply emergency braking in advance and prevent a tragedy;
covers - are installed at the intersection of public railway tracks with the railway tracks of various enterprises, where industrial railway transport also operates, even with tram tracks; in the normal position the traffic light is not on, but if, for example, a train with finished products is coming from a neighboring factory to the station , the traffic light turns red, the order of such interaction is also regulated by the relevant instructions;
warning ones - installed in front of entrance traffic lights in areas not equipped with automatic blocking, the so-called “semi-automatic blocking” is a technical term;
shunting - installed at stations and designed to organize shunting work, signaling with a blue light - stop, passage is prohibited and white - you can move, the route is ready and finally - hump, installed on hump humps at stations, carrying information for the driver of a shunting diesel locomotive.
Shunting traffic light signals
Passage traffic lights are lit with green, yellow and red lights, everything is basically clear, the point here is the so-called “automatic blocking”, which we will talk about later, entrance, exit and route traffic lights are more complex; they signal a whole range of signals that carry a very serious If anyone is interested, I will tell you information about the order of the station and even the speed of movement.
Entrance traffic light
There are also additional entrance traffic lights, for general purposes, but they are used only if the train is following the “wrong path” - a technical term. All these traffic lights can be either mast-mounted (mostly) or dwarf, depending on local conditions.
Locomotive traffic light
And there is another cool traffic light - a locomotive one, installed in the locomotive cabin and duplicating the readings of the traffic light located in front, so here it is. All traffic light signals in encoded form enter the track circuit, and from there, through special receiving coils installed on the locomotive, through a decoder to the locomotive traffic light. Barrier and cover traffic lights are also involved in the rail circuit, so that the driver already knows about the obstacle to movement in advance, at the locomotive traffic light.
Locomotive traffic light coil. Reads electromagnetic codes from the rail and transmits them to the locomotive traffic light decoder.
Shunting signals are not included in the rail circuit and their signals are not displayed on the locomotive traffic light.
Best wishes!