Every citizen of our country who has received a license to drive a vehicle, when getting behind the wheel, understands the full share of his responsibility for non-compliance with traffic rules - traffic rules. Transport management requires not only knowledge of traffic rules, but also mandatory compliance with them.
By becoming a participant in road traffic, the driver enters an area of general rights and obligations, where the traffic police monitor compliance with traffic rules and order on all roads. Drivers are not always disciplined, sometimes they commit what they consider to be minor violations, but at the first request of a traffic police officer they are required to stop and present documents for the right to drive. If violations are detected that do not lead to serious problems, the violator will be fined in the prescribed amount. Every year, the requirements and penalties become more stringent, and fines issued must be paid within the deadlines established by law.
Responsibility for violating traffic rules
About compliance with traffic rules
Pedestrians, for example, crossing the road, also enter a responsible traffic zone and are required to follow specific rules of conduct defined in clause 1.2 of the traffic rules. They may be subject to a fine of 500 rubles for violating crossing rules, for example, in the wrong place or for driving through a red traffic light and other offenses that do not lead to serious consequences.
Important! The passenger is also responsible if he does not wear a seat belt. He will pay a fine of 1,000 rubles, just like the driver of the car.
Drivers, pedestrians, passengers who violate traffic rules, causing tragedies of varying degrees of severity, may be held accountable:
- civil, based on Chapter 59 of the Civil Code (Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- administrative, which is regulated by Article 12.30 of the Code of Administrative Offenses (CAO RF);
- criminal, based on Article 266 of the Criminal Code (Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Violation of traffic rules is subject to punishment, which depends on the severity of the offense.
Responsibility and its extent are determined by a court decision when the violation or crime committed is proven. In our country there is a principle of “presumption of innocence”. Proving the guilt of the offender is the responsibility of the traffic police, law enforcement agencies and the criminal investigation department. Everyone must understand that when entering into traffic relations, ignorance of traffic rules, violations of the established rules through negligence or inattention do not exempt from liability.
Traffic police officers are the first to stop and record violations on the road. To prove and determine the degree of guilt, they can use a single driver’s database, photos, videos, DVR data, and witness testimony. They have the right to issue a fine within the limits of their powers. They are defined in the Administrative Regulations of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation by order of the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate No. 185 dated October 20, 2017. These regulatory documents set out a clear procedure for employees, which they are obliged to follow under any circumstances. It will not prevent drivers from becoming familiar with them, which will help them understand the limits of what is permissible in communicating with the inspector.
Important! All collected evidence will help in court and administrative commissions to make a final decision and determine the degree of guilt of the offender.
Traffic police officers have the right to issue a fine
Important documents regulating the resolution of emergency situations on all roads in our country are OSAGO and CASCO policies.
- OSAGO policy is compulsory insurance of automobile and civil liability, in accordance with Federal Law No. 40 of April 25, 2002. The driver’s responsibilities include obtaining and concluding an agreement listing persons with the right to drive a vehicle. Without a policy, no one should get behind the wheel or operate a personal vehicle under any circumstances. These even include the need to register the car with the traffic police and drive it from the car dealership.
In the event of force majeure situations, an MTPL policy will help drivers save money, as well as save time and nerves. According to the new rules, in the absence of a policy, the inspector cannot confiscate the driver's license and send the vehicle to a penalty parking lot, but he can issue a fine, and more than once.
OSAGO is mandatory for all drivers
In the event of an accident, if you have a compulsory motor liability insurance policy, the injured party will be reimbursed for the following expenses:
- up to 400 thousand rubles when causing damage to transport and other means of the injured party;
- up to 500 thousand rubles, if the accident caused harm to the life and health of the victim.
Every driver must understand that by concluding an agreement on obtaining a compulsory motor liability insurance policy, he insures not only his car, but also compensation for damage to the injured party.
- The CASCO policy is not mandatory, unlike the MTPL policy. Each driver has the right to independently determine the need to purchase it. It is important to know that with such insurance, damages are paid in case of damage to the car or its theft. This is especially true for beginners who have no driving experience, or owners of expensive luxury cars.
It is not necessary to apply for CASCO insurance, but any driver can do so if desired.
Who got into the camera
The absolute leader in the number of detected violations remains speeding. In total, 124 million orders were issued for this last year.
13.6 million fines were issued for non-compliance with signs or markings.
Car owners were prosecuted 5.2 million times for running a prohibitory traffic light or making a prohibitory gesture from a traffic controller.
Car owners were charged 2.9 million times for violating the rules for placing a vehicle on the roadway, passing oncoming traffic or overtaking.
2.8 million citations were issued for driving a defective vehicle. What is especially important is on the eve of the entry into force of amendments to the law on technical inspection.
Failure to wear seat belts and helmets resulted in 2.6 million citations.
The same number of times last year drivers were cited for driving without compulsory motor insurance.
People who failed to give way to special vehicles were cited 1.9 million times. Pedestrians for traffic violations - 1.4 million times.
The number of violations detected by one camera is becoming smaller every year
Drivers were punished 1.2 million times for failing to give the right of way to pedestrians or other road users.
It is clear that cameras are not yet able to issue fines to pedestrians. This is done by road inspectors. However, the Ministry of Internal Affairs did not announce the total number of violations, including those recorded by inspectors.
But it is not difficult to calculate, taking into account the trends of past years, how many violations were identified. Every year, the number of violations detected by inspectors decreases compared to those detected by cameras. If in 2019 inspectors identified only 14 percent of the total number of violations, then with such detection decreasing each year by 1-1.5 percent, we can assume that this year the total number of fines issued was 163-164 million.
Also, cameras cannot detect drunk drivers. It is noteworthy that the number of drivers caught in this state is stable.
A total of 550.7 thousand were identified whose intoxication was confirmed, including those who refused a medical examination. The increase was 0.3 percent.
The number of people found to be under the influence of drugs increased by 5.1 percent and amounted to 22.4 thousand.
The number of drivers repeatedly caught by inspectors while drunk also remains stable. Last year, 68.4 thousand criminal cases were initiated for such violations. The increase was just over half a percent.
Let us recall that the State Traffic Inspectorate has repeatedly said that the number of fines is growing every year not because drivers more often violate traffic rules, but because of the regular increase in the number of automatic photo-video recording systems. At the same time, the number of violations detected by one camera is becoming smaller every year.
When does civil liability arise?
Civil liability occurs in the event of damage to the car, in which compensation for material and moral damage, according to Article 1079 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, is assigned to the person responsible for the accident. Moreover, if both parties have a compulsory motor liability insurance policy, then the restoration of the car and compensation for the costs of restoring health or burial in the event of death are compensated by insurance companies. If these amounts are insufficient, additional costs will be covered by the guilty party. Restoration of damage to your own vehicle is subject to the person responsible for the accident or at the expense of the insured amounts of the CASCO policy, if available.
Important! If the parties disagree about the degree of guilt, the issue is resolved in court, which in its verdict will be based on the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
When the culprit of the accident was driving a company car, the firm, the owner, will bear civil liability, who can then recover damages from the at-fault employee. In case of harm to the health or death of the victim, the culprit himself bears criminal liability, and not the owner of the vehicle.
If the culprit of the accident was driving a company car, the company where he works will bear civil liability.
If the culprit of the accident illegally took possession of the vehicle, or simply stole the car, then the owner, upon presentation of evidence, is released from liability, and the blame falls entirely on the thief. There are situations when a vehicle involved in an accident is registered with a citizen, but as a result of the purchase and sale transaction no longer belongs to him.
Important! In these cases, it is important to understand who owns the car and who owns it.
The same article of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation defines the concept of “force majeure”, in which the owner is released completely or partially from liability for damage that arose due to force majeure or without special harm to the victim. Such insurmountable circumstances include:
- earthquake, tsunami;
- a hole dug on the road without installed warning signs;
- incorrectly installed road sign;
- the owner of the car deliberately created an emergency situation;
- and much more, provided it can be proven.
In the event of an accident due to force majeure, most likely, no one will be held responsible, and the insurance company will pay compensation
When does administrative responsibility arise?
The driver violated traffic rules and was stopped by a traffic police officer to be held accountable in strict accordance with the Code of Administrative Offenses (CAO), in which all violations are clearly prescribed a specific article under which administrative punishment is imposed.
Important! Article 3.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses states that an administrative measure is intended to establish state responsibility for a committed violation of rights and obligations by a citizen, and serves the purpose of preventing him from further committing similar actions.
Administrative punishment does not serve the following purposes:
- humiliate a person by issuing any punitive verdict provided for by the Code of Administrative Offences;
- physical impact on the offender;
- cause business harm to the violator's reputation.
In some cases, administrative liability arises
The Administrative Code (CAO) provides for up to nine subtypes of punishments, which can be divided according to criteria.
- Punitive measures against offenders:
- warning is a moral, right action;
- penalties, seizure of property with confiscation - this is a monetary and property impact;
- arrest for 15 days, deportation from the country - this is a restriction of freedom of action, temporary or permanent;
- confiscation of a driver's license is a forced qualification measure, temporary cessation of activity.
The driver's driving license may be revoked
- Corrective influences:
- fine, arrest, disqualification are educational and corrective measures;
- confiscation is a measure to prevent similar violations in the future.
How do punishments differ in duration and terms of execution?
- A fine, warning, confiscation, withdrawal of rights, administrative expulsion are one-time, one-time penalties.
- Arrest for 15 days, disqualification, deprivation of special rights - these are different punishments in terms of duration.
In case of particularly serious violations, even arrest for 15 days is possible.
Let's look at the most commonly used measures of administrative penalties for violations and accidents on the roads. The measures apply not only to drivers, but also to passengers, pedestrians, and other road users.
Warning (Article 3.4 of the Administrative Code)
If the violation does not have aggravating consequences, the inspectorate officer draws up a written protocol on the administrative violation. A warning is written in it and entered into the traffic police database. If this happens again, a fine will be issued.
The warning is of a moral and educational nature and is a warning against repeated traffic violations. It is an independent type and is valid for one year. Such preventive measures are prescribed mainly for minor legal violations, most often to minor teenagers and to persons who have committed an unlawful violation for the first time.
A warning is issued for minor violations
Important! A warning is issued to both individuals and legal entities.
Administrative fine (Article 3.5 of the Administrative Code)
Based on Chapter 12 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the table of fines is updated once a quarter. It was last updated with changes on April 24, 2019. The list of fines can be found on the official website of the traffic police.
In case of a certain violation of traffic rules, a fine of 3 MCI is issued. If the violator does not dispute the fine, then he is given a 50% discount, and the amount must be paid within 7 days.
Important! The fine is limited to 100 rubles. up to 5000 rub. for individuals, up to 50,000 rubles. for executives and up to a million for legal entities.
A decision to impose a fine may be made by a court authorized by the administrative commission. In case of violation by individuals, it is permissible to impose and collect a fine by a traffic police inspector.
The fine can be issued by a traffic police inspector or imposed in court.
Revocation of driver's license
Deprivation of a driver's license is possible:
- for driving while drunk - if the blood level is more than 0.35 ppm, imprisonment is imposed for up to a year;
- for driving a car or other transport without license plates or with them, but fake ones - for a period of up to 3 months.
- for the use of sound sirens and flashing lights without permission - for a period of up to a year;
- for exceeding the speed of up to 80 km - for up to six months;
- when driving onto a tram path or into oncoming traffic - for up to a year.
- for deliberate failure to provide free passage for special transport: ambulance, fire, police - up to a year.
- for the transportation of dangerous and large-sized cargo without special permission from the traffic police - for a period of up to a year.
In some cases, rights are deprived
Arrest for 15 days
For whom is this punishment possible?
- drivers deprived of their licenses drove while intoxicated;
- drivers did not pass or refused to undergo a medical examination for alcohol intoxication;
- drivers who fled the scene of an accident;
- malicious defaulters of traffic police fines.
In case of leaving the scene of an accident or refusing a medical examination, arrest for 15 days is possible.
Traffic violations
Hello, dear readers! Today, let's dwell a little on violations of traffic rules. Let's talk about offenses on the road, which, unfortunately, are often committed deliberately.
The question here is, why do we strive not to break the law not related to traffic, but on the road we behave differently? Perhaps one of the reasons (namely, only one of the reasons) for traffic violations is related to the provided liability for these violations. Look what the most common punishment on the road is, that’s right, many violations, let’s say, today cost 500 rubles, and when they also offer us to pay in the first 20 days and get a discount, even what a 50%! Many have heard that the possibility of paying only 1/3 of the fine for some, as they say “frivolous” violations, is being considered. It turns out that only by violating the Rules three times will the full amount of the prescribed administrative fine for the offense be released.
The Government’s position with such proposals is not very clear. From TV screens, newspaper pages, and the Internet, we are constantly given terrible figures about what is happening on the roads. And in such a situation, “meeting” the violators (by introducing preferential terms for repaying the fine) is definitely wrong. Sometimes one gets the impression that the goal is different, to replenish the budget by any means (it’s good if I’m wrong). With the numbers on road accidents that are being announced, it’s time to tighten penalties for violations of traffic rules. Below is a table from the traffic police website with traffic accident statistics for the period from January to October 2021, in fact very scary numbers behind which lie human lives and destinies.
1.1. These Rules of the Road (hereinafter referred to as the Rules) establish a uniform procedure for road traffic throughout the Russian Federation. Other regulations relating to road traffic must be based on the requirements of the Rules and not contradict them.
1.3. Road users are required to know and comply with the relevant requirements of the Rules, traffic lights, signs and markings, as well as comply with the orders of traffic controllers acting within the limits of the rights granted to them and regulating traffic with established signals.
1.5. Road users must act in such a way as not to create a traffic hazard or cause harm.
1.6. Persons who violate the Rules are liable in accordance with current legislation.
Let’s not dwell now on tightening liability for persons under the influence of alcohol; there are correct steps in this direction.
We are talking about something else, why at some point they decided that speeding (Exceeding the speed limit can lead to an uncontrolled skid and loss of control over the car, it’s good if the car just ends up on the side of the road, but what if there’s an oncoming lane?) by 10 km/h It’s not very scary and the punishment is a fine of 100 rubles, which is a small number. Let's "officially" allow it to exceed 20 km/h (in reality, even 22 km/h, don't forget about the error), some people really think that since there is no punishment, it means it is allowed to violate, although in the Rules, everything is as before.
10.1. The driver must drive the vehicle at a speed not exceeding the established limit, taking into account the intensity of traffic, the characteristics and condition of the vehicle and cargo, road and meteorological conditions, in particular visibility in the direction of travel. The speed must provide the driver with the ability to constantly control the movement of the vehicle to comply with the requirements of the Rules.
What is 100 rubles, let there be a tolerance of 20 km/h and a fine of 500 rubles. Or maybe it was necessary to leave it at 10 km/h, but the penalty for exceeding it should have been set at 5,000 rubles. You can refer to the experience of our neighbors, for example, in the Republic of Belarus:
Administrative liability for offenses against traffic safety and operation of transport in the Republic of Belarus.
Article 18.13. Exceeding the speed limit.
1. Exceeding the established speed by a person driving a vehicle from 10 to 20 kilometers per hour.
Punishment: fine up to 1b.v. (1 base value = 21 BYR = 692.51 RUB as of November 26, 2016)
2. Exceeding the established speed by a person driving a vehicle from 20 to 30 kilometers per hour.
Punishment: fine from 1 to 3b.v.
3. Exceeding the established speed by 30 or more kilometers per hour by the person driving the vehicle.
Punishment: fine from 3 to 10b.v.
4. Actions provided for in parts 2 and 3 of this article, committed repeatedly within one year after the imposition of an administrative penalty for the same violations.
Punishment: fine from 5 to 15 b.v. or deprivation of the right to drive a vehicle for up to 1 year .
As we see, in the Republic of Belarus, the punishment for speeding is quite serious. If you consider that for repeatedly exceeding the maximum speed by 20 km/h within a year, you can even lose your driver’s license for one year, then you definitely won’t want to break the speed limit again.
You may ask, how do you drive then? The answer is according to the Rules of the Road! And I am sure that the likelihood of such a punishment would stop many from violating the Rules. Let's see, today, at intersections equipped with video recording cameras, people often stop or start moving on red, how many allow themselves to cross the stop line at a prohibitory traffic light? Now this is rare, one might say an accident. And now, let's look at the intersections that the automatic video recording system has not yet reached, everything is as before, we start moving not to our green, but to the red of pedestrians, and finishing on the red is often a common thing. And again, what is the penalty for this violation?
12.12 part 1. Driving through a prohibiting traffic light signal or a prohibiting gesture of a traffic controller, except for the cases provided for in part 1 of article 12.10 of this Code and part 2 of this article.
Punishment: administrative fine in the amount of one thousand rubles.
The punishment is only one thousand rubles, but how many lives can running a red light ruin?
Look at another article of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
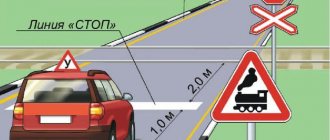
12.10 part 1. Crossing a railway track outside a railway crossing, entering a railway crossing with a closed or closing barrier or when there is a prohibiting signal from a traffic light or a crossing officer, as well as stopping or parking at a railway crossing
Punishment: an administrative fine in the amount of one thousand rubles or deprivation of the right to drive vehicles for a period of three to six months .
I am sure that if the law provided for such liability for driving through an intersection at a prohibitory traffic light, many road users would think about whether it is worth breaking the Rules.
And again to punishment for such a violation in the Republic of Belarus.
Article 18.14. Failure to comply with traffic control signals, violation of passenger transportation regulations or other traffic regulations.
1. Failure of a person driving a vehicle to comply with the requirements of signals, instructions of a traffic light or a traffic controller, except for the cases provided for in Article 18.15 of this Code.
Punishment: from 1 to 5 b.v. (maximum penalty for violation 5b.v = 105 BYR = 3,462.53 RUB as of November 26, 2016)
It is clear that increasing the amount of fines for violations of traffic rules will not solve the problem, but it will definitely reduce the number of violations.
Changing our modern mentality* and not just one person, but the whole society can change, turn the situation in the right direction!
*Great Soviet Encyclopedia
MENTALITY - (mentality) (from Late Latin mentalis - mental), way of thinking, a set of mental skills and spiritual attitudes inherent in an individual or social group.
When working and teaching driving skills, you often observe how people who are previously far from understanding road traffic in accordance with the Rules, at the initial stage of joining the community of motorists, often perceive other people’s violations with criticism. Unfortunately, only at the beginning of your long journey along the roads, then everything falls into place. We get behind the wheel of our vehicle and strive to become like everyone else (in this case, I don’t mean all road users).
Maybe it's time to ask yourself these and other questions:
- How can driving through an intersection with a prohibitory traffic light result?
- What can lead to driving through solid markings into the oncoming lane?
- How can driving over the speed limit end?
I am sure that everyone knows the answers to these questions and not only know, but have also seen the results of such violations. I don’t want to say that all road users grossly violate the Traffic Rules, but most of us, unfortunately, allow ourselves not these, but other violations (violation of stopping and (or) parking rules, violation of turning rules, violation of the location of the vehicle on roadways and others...).
And the most important question:
Why do I allow myself to break traffic rules?
All of the above, unfortunately, takes place on our roads. Maybe it's time for us to start changing, albeit in small steps, but to start moving in the right direction. Towards road safety! Good luck to everyone on the road!
Examples
Let's look at examples of violations and the subsequent administrative penalties that apply for them.
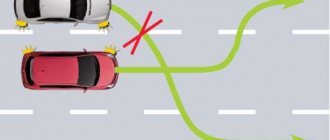
- When crossing a solid line marking, when the driver changes lanes, he is issued a warning for the first time, and for repeating the violation - a fine of 500 rubles.
- If the driver entered the oncoming lane while crossing a solid line, the punishment is much more severe: 5,000 rubles. or possibly deprivation of rights for up to six months.
- The driver ignored the "brick" sign. I drove down a one-way street facing traffic. For this he faces the deprivation of his driver's license for six months. And if this violation occurred on the site, you can receive a warning.
There is a penalty for driving under a brick
- For improper tinting of windows, a fine of 500 rubles is imposed. Until 2014, the fine was very severe: the driver was fined and the car was impounded.
- For the absence of a compulsory motor liability insurance policy or if you have one that has not been renewed on time, a fine of 800 rubles is imposed, which can be charged every day every time the vehicle is stopped by an inspector until the receipt of the policy.
- According to Art. 12.27 of the Code of Administrative Offences, the driver does not have the right to leave the scene of an accident, otherwise for unjustified leaving the scene of the accident he will be deprived of his license for up to one and a half years. Arrest for 15 days may also be applied. Clause 2.5 of the traffic rules lists how a driver should behave in the event of an accident: stop, turn on the hazard lights, place a sign behind the car warning of an accident, call an inspector and wait without moving objects. If possible, take photos and videos and stop witnesses.
As an exception, the rules provide for the opportunity to leave the scene of an accident by mutual agreement with other participants in the incident in the absence of mutual claims, without calling an inspector.
Important! Drivers must exchange waivers and exchange addresses and phone numbers.
As a rule, leaving the scene of an accident is not allowed
- It is possible to detain a vehicle and send it to an impound lot or block one wheel for driving while intoxicated, as well as if the driver does not have a driver’s license with him, and no matter for what reason. If they are lost, it will take a long time to recover them.
- According to Art. 12.8. of the Code of Administrative Offenses, driving while intoxicated entails a fine of 35 thousand rubles and deprivation of rights for up to two years. The inspector determines the driver's drunken state by external signs and suggests saying certain words or walking in a straight line. If the suspicions are confirmed, he will offer to undergo examination at the place of stop using a breathalyzer. If they disagree, the person is sent for a compulsory medical examination.
Drunk driving is strictly punishable
Types of liability for violation of traffic rules: administrative
Administrative punishment can be imposed in the form of:
- warnings;
- fine;
- deprivation of the right to drive a vehicle;
- administrative arrest or confiscation of the vehicle itself if it became an instrument of crime.
Regulated by articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (12.24 and 12.8).
The articles provide for punishment for causing minor damage to the health of the victim in the form of a fine in the amount of 2500-5000 rubles. The driver can also voluntarily refuse to drive a car for a period of 12 to 18 months.
Harm to human health assessed as moderate severity entails a fine of 10 to 25 thousand rubles or refusal to drive for a period of 1.5 to 2 years.
Drivers who commit road accidents while intoxicated are punished much more severely. If the inspector proves that a person was driving a car (motorcycle, bus, etc.) while intoxicated, then the offender faces a fine of 30-50 thousand, deprivation of rights for a period of 1.5 to 3 years and administrative arrest for 10-15 days.
When does criminal liability occur?
Road accidents are very dangerous not only because of damage to vehicles, but also because people suffer, receiving injuries and injuries, and the worst thing is that they can lead to death. This is a consequence of the driver’s irresponsibility, violating traffic rules, or improper maintenance of the vehicle. Such carelessness can lead to administrative and criminal liability. The extent of such liability depends on the nature of the injuries inflicted on people, which are assessed according to the criteria of forensic medical examination.
Important! Responsibility under the Code of Administrative Offenses will follow for the actions of the accused that led to slight harm to the victim’s health without serious consequences, as well as to moderate harm to health with loss of up to 33% of the ability to work and long-term treatment for more than 21 days.
Both administrative and criminal liability are possible for causing harm to health.
The signs of criminal liability under Article 264 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation include:
- infliction of grievous harm to the victim's health with subsequent disability of various groups;
- injuries leading to the death of one or more persons, which is a particularly aggravating consequence;
- when the culprit himself had the opportunity to provide all possible assistance, but knowingly left the injured person in a life-threatening condition;
- for driving any vehicle by a drunk driver or a person under the influence of drugs;
- an accident that occurred due to poor quality repairs of the vehicle;
- falsification or destruction of an identification number assigned by the traffic police or its use for criminal purposes;
- forgery of a driver's license or use of a knowingly forged driver's license;
- theft or theft of a vehicle.
Some offenses are punishable under the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation
All criminal cases are tried in court in the presence of representatives of the prosecutor's office, prosecutors, and a lawyer as a defender of the rights of the accused. During the trial, the circumstances of the criminal act presented by the investigation are thoroughly studied. The judge, based on the criminal code, depending on the severity of the crime, can impose the following types of punishment:
- impose a sentence of six months, one year and up to seven years. Establish deprivation of the right to be appointed to certain positions for a period of up to three years;
- restriction on conducting a certain type of activity for a period of up to three years;
- forced performance of compulsory work lasting up to 480 hours;
- detention and imprisonment for a term of six months to a maximum of 7 years.
For certain offenses, serious penalties are possible, including imprisonment for several years.
What innovations have been introduced in 2021?
Since January 1, 2019, a unified register of those who have been trained in driving schools has been created and is already operating to combat the forgery of driver’s licenses.
From 01/01/2019, payments for all types of regular urban passenger transportation of people and luggage were exempt from VAT.
From 01/01/2019, all traffic police fines will be used only for road repairs - now they will not be transferred to other regional expenses.
As of January 7, 2019, a decision was made to restore discounts on traffic police fines.
Since 01/09/2019, significant amendments have been made to the design of the MTPL policy.
2021 has seen many changes in traffic laws
From 03/01/2019, licensing was introduced for buses carrying passengers, including registered ones, as well as those used for the own needs of organizations.
From March 28, 2019, to prevent violations, automatic detection systems for crossing violations should appear at all public railway crossings.
From April 15, 2019, owners of stolen cars were exempted from transport tax.
From April 24, 2019, the punishment for violators who leave the scene of an accident will be tougher. They face imprisonment from 4 to 9 years, depending on the severity of the offense, especially if the victim was in a severe unconscious or weakened state.
As of May 1, 2019, a new GOST was introduced with a reduction in the size of road signs.
Disciplinary types of liability for violation of traffic rules
This type of disciplinary liability for violating traffic rules can only be applied to employees of enterprises. In this case, the punishment is imposed by the employer himself. Depending on the severity of the act, he may apply measures such as a reprimand or reprimand. For particularly serious violations of discipline, an employee may be dismissed under Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.