If you have a car, you should know
Upon completion of vehicle registration, the motorist assumes obligations for the mandatory payment of transport tax.
Therefore, all citizens and organizations with personal vehicles must inform their regional branches of the Federal Tax Service about the fact of acquisition and ownership of vehicles.
Everyone knows that if you do not pay transport tax, the law imposes certain fines. But not everyone knows what consequences non-payment of transport tax has and what should be done to avoid sanctions.
We will tell you in detail: what are the deadlines for repaying this tax in 2021 and are there any important nuances in this issue that require particularly close attention?
Transport tax hot spots
All individuals who are the proud owners of motorcycles, cars, scooters, yachts, snowmobiles and self-propelled vehicles - all, without exception, must pay transport tax.
The amount of this tax does not have a fixed amount and is completely dependent on the region that establishes it. Regions set the amount based on the general economic situation.
The amount of this tax directly depends on:
- engine power;
- type of vehicle;
- vehicle capacity;
- cost of the car.
Therefore, regardless of the fact which vehicle is registered with the citizen, he will pay tax even if he does not use his vehicle and it is in his garage.
For some period of time, tax officials received information about citizens’ means of transportation through special companies involved in the process of registering vehicles. But this was associated with a number of inconveniences.
Therefore, now there is a different scheme for informing the Federal Tax Service: information to the tax authorities is provided directly by the owner of the car.
Important information! Upon completion of the transfer of information about the car to the tax authorities, the owner of the car will receive a receipt at home with the amount of payment. There is no need to do the calculations yourself.
Transport tax: different and on time
The amount of this tax is always different. It depends on the type of vehicle, the power of the car, etc. As a rule, when calculating the final figure, the following important points are taken into account:
- Indicators reflected in the technical documentation for the vehicle. This is motor power information measured in horsepower.
- Tax rate per horsepower. It varies depending on the region. The unit strength indicator is multiplied by the total number of forces.
- How many months during the year did the vehicle belong to the owner?
Important information! Back in 2021, the time frame for repaying the transport duty was shifted upward, until December (previously the time threshold ended at the beginning of November). Repayment of the tax duty is always carried out by the owner of the vehicle in accordance with the clear instructions of the notification information from the tax authorities.
Non-payment: Do you need this?!
As the owner of a car, it is necessary to memorize the entire list of possible sanctions provided for by law in relation to transport tax evaders.
In the list of main sanctions provided by the state, the following measures are particularly “popular”:
- Calculation of a fine.
- Accrual + deduction of penalties.
- Seizure of the defaulter's property.
- Seizure of funds to cover a debt.
- Imposing a ban on crossing the border.
- Withholding a certain amount of money from your salary, credited to a bank plastic card.
In the case when tax authorities sue, collecting all outstanding amounts, fines and penalties through court decisions, it is necessary to understand that they are acting within the framework of the law.
The scope of penalties varies and depends on the period of non-payment and all the nuances outlined above. Inspectors, when assessing sanctions, always follow the rule: the penalty amount for late payment of the automobile duty can be accrued only for a period of three years, but no more.
Attention! A statement of claim can be drawn up and sent only when its amount exceeds 5,000 rubles.
The lawsuit is also limited in time: it must be filed no later than six months after all the allotted deadlines for payment have passed. And if the tax authorities missed this time period, then resolving the issue can be very difficult.
Attention! The amount of the penalty is calculated in the amount of 20% of the total volume of the calculated debt. In the case where there is evidence that non-payment of tax was intentional, the amount is doubled, reaching 40%.
Many debtor owners are worried and ask whether their car can be seized for transport debts?
According to the letter of the law, the court may well seize the vehicle. Therefore, neglecting to pay the car duty can cause many problems, restrictions and expenses for a citizen.
We remind you that even if you thoroughly study all the data that is in the public domain, this will not replace the experience of professional lawyers! To get a detailed free consultation and resolve your issue as reliably as possible, you can contact specialists through the online form .
What are the consequences of non-payment?
Every person who has a personal vehicle at their disposal should know what sanctions may be imposed for tax amounts not received within the established time frame.
Among the main penalties that are imposed due to non-payment of taxes, the following punishment can be noted:
- imposition of a fine;
- accrual and deduction of penalties;
- seizure of the property of a citizen who owes;
- withdrawal of cash to pay off debt;
- ban on traveling to the border;
- deduction of a certain amount from the monthly salary, which is credited to the bank card.
If the tax office has filed a lawsuit and demands the collection of all unpaid amounts, as well as fines and penalties through regional courts, it is worth knowing that it has every right to do so.
The size of this amount may be different; it varies directly depending on the time of delay and the points listed above. When calculating, the rules are used - a fine for non-payment of transport tax is assessed only for the last three years, no more.
A claim can be drawn up and sent only if its amount is more than 5,000 rubles.
An application to the court also has special time limits; it can be filed with the court no later than 6 months after all due and stated deadlines for payment have expired.
If a tax organization missed this deadline for some reason, it will not be easy to achieve a resolution of the issue.
If you are interested in the question regarding the amount of the fine, then it can be noted that it is calculated at 20% of the amount of the accrued debt.
If during the trial it was proven that the tax and the assigned penalty for non-payment of transport tax were not paid intentionally, then the consequences of non-payment of transport tax can be increased to 40%.
Many people are interested in whether a car can be seized for non-payment of transport tax. Here we can give a positive answer - the court may well make a similar decision.
As can be seen from all of the above, the liability for non-payment of transport tax by an individual is quite serious.
Video: What are the consequences of failure to pay transport tax?
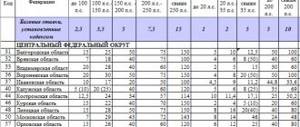
Penalty: calculation formula
In the event that an individual’s annual payment is overdue, a daily penalty is charged, which goes to the state treasury, as well as the transport tax itself.
The amount of the daily penalty is calculated using the exact equation:
| Penalty calculation formula | Explanation of meanings |
| NS x PS x 1/300 x D | TS is the amount of unpaid transport tax; PS is the interest rate of the Central Bank; 1/300 is the interest rate of penalties according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; D is the number of days overdue. The calculation is carried out strictly from the moment the debt is formed and ends on the day of its payment. |
Starting from 2021, the amount of the refinancing interest rate is equal to the key rate of the Central Bank. This information is located on the Bank of Russia portal.
To better understand this theory, let's give an example:
A certain Ivanov has a delay in transport tax for a period of ten days, with a fixed tax amount of 5,000 rubles. If you calculate the penalty using this formula, you get an amount equal to 127.5 rubles (5000 x 8.25% x 1/300 x 90 days).
Note! First of all, you need to pay off the full amount of the fee on the receipt. Then, after waiting for the money to be credited to the unified tax database, you will have to pay penalties. This is the only way to stop the accrual of penalties for the time the payment was credited to the Federal Tax Service database.
It must be kept in mind that if a car is purchased, but the payment receipt for the next year has not arrived, you should immediately contact the tax office and inform it about the data on the car strictly before December 31.
Otherwise, a fine will be imposed on the owner of the vehicle.
Bailiff with a baton
A real hunt has begun in the country for debtors who “forget” to pay taxes on time. Mobile groups are created from representatives of different departments with different powers, which, by combining these powers, literally take to the high road.
As a result, unscrupulous taxpayers, fine and alimony payers find themselves driven into impound lots: either immediately pay the state, or say goodbye to the seized property.
The action plan is simple. The police stop the car, the tax officer checks the database to see if such and such a citizen is listed as a debtor, and the bailiff, in accordance with the law, may demand payment of the debt or seize property. Particularly obstinate ones are intimidated by the possibility of sending the car to the impound lot until all debts are paid off. But, as a rule, it doesn’t come to this. Debtors either pay in cash or pledge smaller property to the bailiffs—a radio, a telephone, a spare tire.
The fact is that many people have meager debts, at least significantly less than the cost of the car. But it also happens differently. For example, during one raid carried out by three services in Vladivostok, a transport tax evader was detained in an expensive jeep. His debt was 22 thousand rubles. In such cases, the bailiffs do not stand on ceremony. The offender’s car is seized, but the vehicle is handed over to the owner for safekeeping. This means that the would-be owner cannot sell or donate his car. And one of the residents of Kirov owes as much as a million rubles in transport tax.
The results of such joint raids by tax collectors are inspiring. For example, in the Nizhny Novgorod region, creative teams of bailiffs, tax officers and traffic cops not only fulfilled, but also exceeded the collection plan. Already in the first month of such combined work, more than thirty million rubles were collected from debtors. To date, every second debtor has paid off his fines and obligations.
The same practice exists in the Primorsky Territory. Here, in the first half of 2007, bailiffs, with the help of police officers, recovered more than 450 thousand rubles in 1,855 enforcement proceedings. In addition, the debtors were served with nearly 800 demands to appear before the bailiff.
In the first half of the year, the inter-district department of bailiffs in Kirov was executing almost 2.5 thousand court decisions on the forced collection of transport tax for a total amount of over 18 million rubles. Moreover, a quarter of this amount is owed by 36 residents of the city of Kirov. At this point, the bailiffs, with the help of the traffic police, had already collected 8 million rubles in transport tax, which, by the way, will be used for road repairs.
A test joint raid of the three departments also took place in St. Petersburg. Five tax inspectors and three bailiffs were on duty at the traffic police post together with traffic police officers. During their two-hour duty, they stopped more than 20 vehicles. All of them were selected from cars passing by using the Potok system, which allows you to read the registration number of a moving car and instantly check all the data on the car and its owner. Typically this system is used to search for stolen cars. A database of transport tax debtors was established specifically for the joint raid on Potok.
However, some of the stopped drivers, upon closer examination, revealed other sins. For example, bailiffs checked drivers against a database of writs of execution, as a result of which they caught several alimony debtors. And some of the detainees, in addition to transport tax debt, were found to have failed to pay personal income tax. All defaulters were issued receipts on the spot for payment of taxes and fines, but without any liens or seizures of property. In total, during the period of duty, receipts were issued for hundreds of thousands of rubles. It is planned to conduct two more such raids in the coming days, and in the future make them regular. Therefore, those caught a second time for non-payment are unlikely to be able to bypass the impound lot.
| competently |
As the Federal Bailiff Service explained to RG, the operation in St. Petersburg, when the bailiffs took to the road along with representatives of the tax service and the state traffic police, was an experiment and did not last long.
“Our role was that we checked drivers who owed transport tax,” explained a representative of the bailiff service. “And we were only interested in those drivers in respect of whom court decisions had entered into legal force and enforcement proceedings had been initiated. Then our employees could offer, I emphasize, offer to pay the transport tax on the spot. In addition, there were bailiffs who checked whether the driver was a debtor in other enforcement proceedings, for example, for non-payment of alimony or non-repayment of a loan. They could also be offered to pay the debt on the spot.
Those who refused were not subject to reprisals. Cars were not taken from anyone and were not collected. Yes, they could have arrested the iron horse. But de jure to arrest does not mean to take away. The car could be left to the driver for safekeeping. Hypothetically, if the debt was equal to the price of the car, the car could be picked up and taken to a special parking lot, and this would be within the law. There were no complaints from drivers about the actions of bailiffs. The purpose of the operation was to study whether this form of work was effective and to work out the interaction. We will study this experience. If it is considered successful, we will prepare methodological recommendations exclusively within the framework of the law, for distribution in the regions.
| how do you like this |
Sergey Shapovalov,
legal partner:
- This is again an example of a primarily psychological method of collecting taxes. A taxpayer who is an individual cannot be deprived of his property for non-payment of taxes without a court decision. Accordingly, bailiffs cannot do anything without court decisions. The only thing they have the right to is to talk to the taxpayer.
It’s a different matter if we are talking about taxpayers for whom court decisions have been made. In this case, the bailiffs may have real powers to seize property. To do this, it is enough for the bailiff to have in his hands an unexpired writ of execution from the court, which will indicate the amount of the taxpayer’s debt, and an application from the tax authority to make an inventory and seize the taxpayer’s property.
It is worth noting that, as a general rule, enforcement actions are carried out on weekdays, from 6 a.m. to 10 p.m. local time. At other times, this is possible in exceptional cases and only with the written permission of the senior bailiff. And if, nevertheless, it comes to the inventory and seizure of the property (car) of the debtor, then this will have to happen in the presence of witnesses. A tax inspector cannot be one, but a traffic police inspector may well play this role.
Tatiana Styrova,
Director of the Chamber of Tax Consultants:
- Of course, on the one hand, this is a legal chaos. But we should not forget that in Russia there is no tax culture among the population. And the state has to respond to the fact that the population does not pay taxes with appropriate measures.
Such measures are not applied to bona fide taxpayers. They don’t take too much from us, they force us to do what we are obliged to do. I think that when they start teaching tax law in our schools and institutes, and we begin to understand the responsibilities of the taxpayer from school, as in all civilized countries, then there will be no such methods on the part of the state.
On the one hand, as a lawyer, I cannot help but be indignant at this situation. On the other hand, I understand that in the place of government agencies I would act in the same way. I would not defend the taxpayer for one simple reason - he himself is a violator. That is why such extraordinary “troikas” appear as under Stalin.
When legal entities are “hiding”
Legal entities, unlike citizens, are required to independently calculate the car duty. Accordingly, the Federal Tax Service does not take any part in calculating the amount of taxes.
The basis for the calculation is the information provided by the authorities that registered the car, and based on the results of the tax period, the calculation of the transport duty due for payment is made.
In this case, the tax can be charged only for the actual operation of the car, that is: for how many months the vehicle is registered with the traffic police, exactly that much must be paid.
Note! Unlike ordinary citizens, legal entities pay transport tax by making advance payments.
If taxes are not paid, the Federal Tax Service takes legal action, as in the case of individuals.
Important! Unlike ordinary citizens, the deadline for legal entities depends on the region of registration, and most often falls at the beginning of February of the year that follows the reporting period. The claim has a statute of limitations of six months after the end of the period for paying the tax.
How to check your debt yourself?
Many professional lawyers advise checking the debt yourself in order to protect yourself from possible debt and all the consequences that it may cause.
Here is the simplest method for obtaining such information:
- You must register on the State Services website. For this purpose, personal data, telephone number as well as email address are required.
- Passport details, as well as TIN and SNILS are filled in.
- Select and then click the “Get service” button.
- Studying the returned result.
Payment of debt, if any, can be made at any financial institution or directly on the website using a bank card or in a special mobile application.
To receive simple informational assistance by entering data, entering personal data will be enough; to receive more complex services, it is worth going through a more thorough identification confirmation.