How much does OSAGO cost in 2018?
So, first we will explain how the calculation of the insurance premium (the one that is paid when purchasing a policy) works in accordance with the rules of OSAGO.
- There is a base rate in the form of a price range that the insurance companies themselves have the right to set (but more often maximum values are set),
- And there are coefficients that depend on the data of the drivers allowed to drive and the parameters of the car and which are applied in turn to the base tariff by multiplying the latter by these coefficients.
The increase in the cost of compulsory motor liability insurance this time is due to an increase in the base tariff (in fact, the corridor is simply increasing), as well as several coefficients applied to the base tariff.
The final price of the policy is calculated using the following formulas:
- for passenger cars of individuals : basic tariff x territorial coefficient (region of registration of the owner) x bonus-malus coefficient (accident-free driving) x limited/unlimited insurance x vehicle power x seasonality of use x number of violations in the previous insurance period;
- for passenger cars of legal entities : basic tariff x territorial coefficient (region of registration of the owner) x bonus-malus coefficient (accident-free driving) x age/experience of approved drivers x limited/unlimited insurance x vehicle power x seasonality of use x number of violations in the previous insurance period x availability of a trailer;
- for motorcycles and trucks of individuals : basic tariff x territorial coefficient (region of registration of the owner) x bonus-malus coefficient (accident-free driving) x age/experience of approved drivers x limited/unlimited insurance x seasonality of use x number of violations in the previous insurance period x availability trailer;
- for motorcycles and trucks of individuals : basic tariff x territorial coefficient (region of registration of the owner) x bonus-malus coefficient (accident-free driving) x limited/unlimited insurance x seasonality of use x number of violations in the previous insurance period x availability of a trailer.
A small addition has appeared in the MTPL calculation forums - this is the coefficient of the number of violations. Previously, it was not applied, but at the new rates it will be applied and will always be equal to 1.5 if there were violations of the insurance rules in the previous period:
- if the driver knowingly provided false information when applying for insurance, which affected the reduction in the cost of the policy,
- if the driver deliberately staged an accident or lied about damage information,
- if the driver has been presented with a recourse claim.
So, now let's move directly to the numbers, and in the “was/has become” format we will present all the changes in insurance rates and coefficients!
You will also be interested in:
- OSAGO 2021 – what’s new and what changes?
- How much more expensive will OSAGO insurance be after an accident?
- What changes are being made to compulsory motor liability insurance from April 1, 2021? Will insurance become more expensive?
OSAGO territory coefficient table 2021
Below is a detailed table of coefficients for the MTPL territory in 2021. With its help, you can clarify how the cost of the policy depends on the region in which the vehicle is operated. Please note: for car owners who are individuals, the territorial coefficient is indicated depending on the place of registration of the owner.
| № | Territory of primary use of vehicles | Coefficient for vehicles, excluding tractors, self-propelled road construction and other machines | Coefficient for tractors, self-propelled road-building and other machines, with the exception of vehicles that do not have wheel propulsors |
| 1 | Republic of Adygea | 1,3 | 1 |
| 2 | Altai Republic | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 3.1 | Gorno-Altaisk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 3 | Altai region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 4.1 | Barnaul | 1,7 | 1 |
| 4.2 | Biysk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 4.3 | Zarinsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 4.4 | Rubtsovsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 4.5 | Novoaltaysk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 4 | Amur region | 1 | 0,6 |
| 5.1 | Free | 1,1 | 0,9 |
| 5.2 | Belogorsk | 1,1 | 0,9 |
| 5 | Arhangelsk region | 0,85 | 0,5 |
| 6.1 | Kotlas | 1,6 | 1 |
| 6.2 | Arkhangelsk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 6.3 | Severodvinsk | 1,7 | 1 |
| 6 | Astrakhan region | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 7.1 | Astrakhan | 1,4 | 1 |
| 7 | Republic of Bashkortostan | 1 | 0,8 |
| 8.1 | Kumertau | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 8.2 | Blagoveshchensk | 1,6 | 0,9 |
| 8.3 | October | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 8.4 | Salavat | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 8.5 | Sterlitamak | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 8.6 | Ishimbay | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 8.7 | Tuymazy | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 8.8 | Ufa | 1,8 | 1 |
| 8 | Belgorod region | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 9.1 | Belgorod | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 9.2 | Gubkin | 1 | 0,8 |
| 9.3 | Stary Oskol | 1 | 0,8 |
| 9 | Bryansk region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 10.1 | Klintsy | 1 | 0,8 |
| 10.2 | Bryansk | 1,5 | 1 |
| 10 | The Republic of Buryatia | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 11.1 | Ulan-Ude | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 11 | Vladimir region | 1 | 0,8 |
| 12.1 | Vladimir | 1,6 | 1 |
| 12.2 | Gus-Khrustalny | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 12.3 | Moore | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 12 | Volgograd region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 13.1 | Volgograd | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 13.2 | Volzhsky | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 13.3 | Kamyshin | 1 | 0,8 |
| 13.4 | Mikhailovka | 1 | 0,8 |
| 13 | Vologda Region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 14.1 | Vologda | 1,7 | 1 |
| 14.2 | Cherepovets | 1,8 | 1 |
| 14 | Voronezh region | 0,8 | 0,6 |
| 15.1 | Borisoglebsk | 1,1 | 0,9 |
| 15.2 | Rossosh | 1,1 | 0,9 |
| 15.3 | Voronezh | 1,5 | 1,1 |
| 15.4 | Liski | 1,1 | 0,9 |
| 15 | The Republic of Dagestan | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 16.1 | Buynaksk | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 16.2 | Derbent | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 16.3 | Kaspiysk | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 16.4 | Makhachkala | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 16.5 | Khasavyurt | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 16 | Jewish Autonomous Region | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 17 | Transbaikal region | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 18.1 | Chita | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 18 | Ivanovo region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 19.1 | Kineshma | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 19.2 | Shuya | 1 | 0,8 |
| 19.3 | Ivanovo | 1,8 | 1 |
| 19 | The Republic of Ingushetia | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 20.1 | Malgobek | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 20 | Irkutsk region | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 21.1 | Cheremkhovo | 1 | 0,8 |
| 21.2 | Shelekhov | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 21.3 | Angarsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 21.4 | Bratsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 21.5 | Irkutsk | 1,7 | 1 |
| 21.6 | Tulun | 1 | 0,8 |
| 21.7 | Usolye-Sibirskoye | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 21.8 | Ust-Ilimsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 21.9 | Ust-Kut | 1 | 0,8 |
| 21 | Republic of Kabardino-Balkaria | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 22.1 | Chill | 1 | 0,8 |
| 22.2 | Nalchik | 1 | 0,8 |
| 22 | Kaliningrad region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 23.1 | Kaliningrad | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 23 | Republic of Kalmykia | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 24.1 | Elista | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 24 | Kaluga region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 25.1 | Kaluga | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 25.2 | Kirov | 1,4 | 1 |
| 25.3 | Obninsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 25 | Kamchatka Krai | 1 | 0,6 |
| 26.1 | Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky | 1,3 | 1 |
| 26 | Republic of Karachay-Cherkessia | 1 | 0,8 |
| 27 | Republic of Karelia | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 28.1 | Petrozavodsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 28 | Kemerovo region | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 29.1 | Osinniki | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 29.2 | Kiselevsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 29.3 | Yurga | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 29.4 | Kemerovo | 1,9 | 1 |
| 29.5 | Mezhdurechensk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 29.6 | Novokuznetsk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 29.7 | Prokopyevsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 29.8 | Anzhero-Sudzhensk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 29.9 | Belovo | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 29.10 | Berezovsky | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 29 | Kirov region | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 30.1 | Kirovo-Chepetsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 30 | Komi Republic | 1 | 0,8 |
| 31.1 | Syktyvkar | 1,6 | 1 |
| 31.2 | Ukhta | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 31 | Kostroma region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 32.1 | Kostroma | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 32 | Krasnodar region | 1 | 0,8 |
| 33.1 | Kropotkin | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 33.2 | Krymsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 33.3 | Armavir | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 33.4 | Kurganinsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 33.5 | Gelendzhik | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 33.6 | Labinsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 33.7 | Slavyansk-on-Kuban | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 33.8 | Krasnodar | 1,8 | 1 |
| 33.9 | Yeysk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 33.10 | Novorossiysk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 33.11 | Anapa | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 33.12 | Timashevsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 33.13 | Sochi | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 33.14 | Tikhoretsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 33.15 | Tuapse | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 33.16 | Belorechensk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 33 | Krasnoyarsk region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 34.1 | Achinsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 34.2 | Zheleznogorsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 34.3 | Lesosibirsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 34.4 | Krasnoyarsk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 34.5 | Minusinsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 34.6 | Norilsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 34.7 | Zelenogorsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 34.8 | Nazarovo | 1 | 0,8 |
| 34.9 | Kansk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 34 | Republic of Crimea | 0,6 | 0,6 |
| 35 | Kurgan region | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 36.1 | Shadrinsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 36.2 | Mound | 1,4 | 0,8 |
| 36 | Kursk region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 37.1 | Kursk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 37 | Leningrad region | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 38 | Lipetsk region | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 39.1 | Dace | 1 | 0,8 |
| 39.2 | Lipetsk | 1,5 | 1 |
| 39 | Magadan Region | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 40.1 | Magadan | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 40 | Mari El Republic | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 41.1 | Volzhsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 41.2 | Yoshkar-Ola | 1,4 | 0,8 |
| 41 | The Republic of Mordovia | 0,8 | 0,6 |
| 42.1 | Ruzaevka | 1,2 | 1 |
| 42.2 | Saransk | 1,5 | 1 |
| 42 | Moscow | 2 | 1,2 |
| 43 | Moscow region | 1,7 | 1 |
| 44 | Murmansk region | 1,2 | 1 |
| 45.1 | Severomorsk | 1,6 | 1 |
| 45.2 | Monchegorsk | 1,3 | 1 |
| 45.3 | Apatity | 1,3 | 1 |
| 45.4 | Murmansk | 2,1 | 1,2 |
| 45 | Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 46 | Nizhny Novgorod Region | 1 | 0,8 |
| 47.1 | Bor | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 47.2 | Vyksa | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 47.3 | Arzamas | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 47.4 | Kstovo | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 47.5 | Sarov | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 47.6 | Dzerzhinsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 47.7 | Nizhny Novgorod | 1,8 | 1 |
| 47.8 | Balakhna | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 47 | Novgorod region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 48.1 | Borovichi | 1 | 0,8 |
| 48.2 | Velikiy Novgorod | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 48 | Novosibirsk region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 49.1 | Kuibyshev | 1 | 0,8 |
| 49.2 | Berdsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 49.3 | Novosibirsk | 1,7 | 1 |
| 49.4 | Iskitim | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 49 | Omsk region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 50.1 | Omsk | 1,6 | 1 |
| 50 | Orenburg region | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 51.1 | Buguruslan | 1 | 0,8 |
| 51.2 | Buzuluk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 51.3 | Orenburg | 1,7 | 1 |
| 51.4 | Orsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 51.5 | Novotroitsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 51 | Oryol Region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 52.1 | Livny | 1 | 0,8 |
| 52.2 | Eagle | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 52.3 | Mtsensk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 52 | Penza region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 53.1 | Kuznetsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 53.2 | Zarechny | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 53.3 | Penza | 1,4 | 1 |
| 53 | Perm region | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 54.1 | Chaikovsky | 1 | 0,8 |
| 54.2 | Krasnokamsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 54.3 | Berezniki | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 54.4 | Lysva | 1 | 0,8 |
| 54.5 | Solikamsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 54.6 | Permian | 2 | 1,2 |
| 54 | Primorsky Krai | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 55.1 | Artyom | 1 | 0,8 |
| 55.2 | Vladivostok | 1,4 | 1 |
| 55.3 | Nakhodka | 1 | 0,8 |
| 55.4 | Spassk-Dalniy | 1 | 0,8 |
| 55.5 | Arsenyev | 1 | 0,8 |
| 55.6 | Ussuriysk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 55 | Pskov region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 56.1 | Velikie Luki | 1 | 0,8 |
| 56.2 | Pskov | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 56 | Rostov region | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 57.1 | Bataysk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 57.2 | Salsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 57.3 | Volgodonsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 57.4 | Gukovo | 1 | 0,8 |
| 57.5 | Novocherkassk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 57.6 | Novoshakhtinsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 57.7 | Azov | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 57.8 | Rostov-on-Don | 1,8 | 1 |
| 57.9 | Taganrog | 1 | 0,8 |
| 57.10 | Kamensk-Shakhtinsky | 1 | 0,8 |
| 57.11 | Mines | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 57 | Ryazan Oblast | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 58.1 | Ryazan | 1,4 | 1 |
| 58 | Samara Region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 59.1 | Chapaevsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 59.2 | Novokuibyshevsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 59.3 | Samara | 1,6 | 1 |
| 59.4 | Sizran | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 59.5 | Tolyatti | 1,5 | 1 |
| 59 | Saint Petersburg | 1,8 | 1 |
| 60 | Saratov region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 61.1 | Volsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 61.2 | Balakovo | 1 | 0,8 |
| 61.3 | Saratov | 1,6 | 1 |
| 61.4 | Balashov | 1 | 0,8 |
| 61.5 | Engels | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 61 | Sakhalin region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 62.1 | Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | 1,5 | 1 |
| 62 | Sverdlovsk region | 1 | 0,8 |
| 63.1 | Upper Pyshma | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 63.2 | Polevskoy | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 63.3 | Verkhnyaya Salda | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 63.4 | Revda | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 63.5 | Ekaterinburg | 1,8 | 1 |
| 63.6 | Mikhailovsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 63.7 | Pervouralsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 63.8 | Asbestos | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 63.9 | Novouralsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 63 | Sevastopol | 0,6 | 0,6 |
| 64 | Republic of North Ossetia-Alania | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 65.1 | Vladikavkaz | 1 | 0,8 |
| 65 | Smolensk region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 66.1 | Vyazma | 1 | 0,8 |
| 66.2 | Roslavl | 1 | 0,8 |
| 66.3 | Yartsevo | 1 | 0,8 |
| 66.4 | Safonovo | 1 | 0,8 |
| 66.5 | Smolensk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 66 | Stavropol region | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| 67.1 | Budennovsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 67.2 | Georgievsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 67.3 | Essentuki | 1 | 0,8 |
| 67.4 | Kislovodsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 67.5 | Nevinnomyssk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 67.6 | Mineral water | 1 | 0,8 |
| 67.7 | Pyatigorsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 67.8 | Stavropol | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 67 | Tambov Region | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 68.1 | Michurinsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 68.2 | Tambov | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 68 | Republic of Tatarstan | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 69.1 | Bugulma | 1 | 0,8 |
| 69.2 | Chistopol | 1 | 0,8 |
| 69.3 | Almetyevsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 69.4 | Leninogorsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 69.5 | Naberezhnye Chelny | 1,7 | 1 |
| 69.6 | Elabuga | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 69.7 | Nizhnekamsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 69.8 | Zelenodolsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 69.9 | Kazan | 2 | 1,2 |
| 69 | Tver region | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 70.1 | Vyshny Volochyok | 1 | 0,8 |
| 70.2 | Rzhev | 1 | 0,8 |
| 70.3 | Tver | 1,5 | 1 |
| 70.4 | Kimry | 1 | 0,8 |
| 70 | Tomsk region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 71.1 | Seversk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 71.2 | Tomsk | 1,6 | 1 |
| 71 | Tula region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 72.1 | Shchyokino | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 72.2 | Efremov | 1 | 0,8 |
| 72.3 | Novomoskovsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 72.4 | Aleksin | 1 | 0,8 |
| 72.5 | Tula | 1,5 | 1 |
| 72.6 | Nodal | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 72 | Tyva Republic | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 73 | Tyumen region | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 74.1 | Tobolsk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 74.2 | Tyumen | 2 | 1,2 |
| 74 | Republic of Udmurtia | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 75.1 | Votkinsk | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 75.2 | Glazov | 1 | 0,8 |
| 75.3 | Sarapul | 1 | 0,8 |
| 75.4 | Izhevsk | 1,6 | 1 |
| 75 | Ulyanovsk region | 0,9 | 0,6 |
| 76.1 | Dimitrovgrad | 1,2 | 0,9 |
| 76.2 | Ulyanovsk | 1,5 | 1,1 |
| 76 | Khabarovsk region | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 77.1 | Komsomolsk-on-Amur | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 77.2 | Amursk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 77.3 | Khabarovsk | 1,7 | 1 |
| 77 | The Republic of Khakassia | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 78.1 | Chernogorsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 78.2 | Abakan | 1 | 0,8 |
| 78.3 | Sayanogorsk | 1 | 0,8 |
| 78 | Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug - Yugra | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 79.1 | Khanty-Mansiysk | 1,5 | 1 |
| 79.2 | Kogalym | 1 | 0,8 |
| 79.3 | Nefteyugansk | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 79.4 | Nizhnevartovsk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 79.5 | Nyagan | 1,3 | 0,8 |
| 79.6 | Surgut | 2 | 1,2 |
| 79 | Chelyabinsk region | 1 | 0,8 |
| 80.1 | Chebarkul | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 80.2 | Satka | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 80.3 | Zlatoust | 1,4 | 0,8 |
| 80.4 | Kopeisk | 1,6 | 1 |
| 80.5 | Magnitogorsk | 1,8 | 1 |
| 80.6 | Miass | 1,4 | 0,8 |
| 80.7 | Chelyabinsk | 2,1 | 1,3 |
| 80 | Republic of Chechnya | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 81 | Chuvash Republic | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 82.1 | Novocheboksarsk | 1,2 | 0,8 |
| 82.2 | Cheboksary | 1,7 | 1 |
| 82.3 | Kanash | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 82 | Chukotka Autonomous Okrug | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 83 | Republic of Yakutia | 0,6 | 0,5 |
| 84.1 | Neryungri | 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 84.2 | Yakutsk | 1,2 | 0,7 |
| 84 | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 1,1 | 0,8 |
| 85.1 | New Urengoy | 1 | 0,8 |
| 85.2 | Noyabrsk | 1,7 | 1 |
| 85 | Yaroslavl region | 0,9 | 0,5 |
| 86.1 | Yaroslavl | 1,5 | 1 |
Increasing the basic MTPL tariff
Here, as we already mentioned above, in 2021 it was not the tariff itself that increased, but the range of possible prices applied by insurers for these tariffs.
| Transport category | Was | It became |
| Motorcycles and scooters (A and M) | 867-1579 | 694-1407 |
| Passenger cars (B and BE) of individuals | 3432-4118 | 2746-4942 |
| Passenger cars (B and BE) of legal entities | 2573-3087 | 2058-2911 |
| Passenger cars (B and BE) taxis | 5138-6166 | 4110-7399 |
| Trucks (C and CE) with a permissible weight of 16 tons | 3509-4211 | 2807-5053 |
| Trucks (C and CE) with a permissible weight of more than 16 tons | 5284-6341 | 4227-7609 |
As you can see, in the basic tariffs, the increase in compulsory motor liability insurance affected only the most popular categories of vehicles: passenger cars. persons, taxi drivers and trucks.
What else is important to know about OSAGO?
As already mentioned, over the past few years, OSAGO has become significantly more expensive due to the rise in the base rate. But it is worth noting that the maximum amount of insurance payment under compulsory motor liability insurance has also increased. If previously only 120 thousand rubles were paid to property when calculating damage and 160 thousand rubles for compensation for damage to life and health, then from 2021 you can receive 400 and 500 thousand rubles, respectively.
The Central Bank also obliged insurance companies to place on their websites online compulsory motor vehicle liability insurance cost calculators, which will allow any citizen to find out the specific price of an insurance policy without leaving home.
Region of residence coefficient
It is correctly called the “territorial coefficient”. And this coefficient was not affected by the increase.
Show odds table
| Region of transport use | Coefficient |
| Republic of Adygea | 1,3 |
| Altai Republic | |
| Gorno-Altaisk | 1,3 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Republic of Bashkortostan | |
| Blagoveshchensk, Oktyabrsky | 1,2 |
| Ishimbay, Kumertau, Salavat | 1,1 |
| Sterlitamak, Tuymazy | 1,3 |
| Ufa | 1,8 |
| Other cities and towns | 1 |
| The Republic of Buryatia | |
| Ulan-Ude | 1,3 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| The Republic of Dagestan | |
| Buynaksk, Derbent, Kaspiysk, Makhachkala, Khasavyurt | 0,7 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| The Republic of Ingushetia | |
| Malgobek | 0,8 |
| Nazran | 0,6 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| Kabardino-Balkarian Republic | |
| Nalchik, Prokhladny | 1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Republic of Kalmykia | |
| Elista | 1,3 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| Karachay-Cherkess Republic | 1 |
| Republic of Karelia | |
| Petrozavodsk | 1,3 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Komi Republic | |
| Syktyvkar | 1,6 |
| Ukhta | 1,3 |
| Other cities and towns | 1 |
| Republic of Crimea | |
| Simferopol | 0,6 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| Mari El Republic | |
| Volzhsk | 1 |
| Yoshkar-Ola | 1,4 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| The Republic of Mordovia | |
| Ruzaevka | 1,2 |
| Saransk | 1,5 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| The Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) | |
| Neryungri | 0,8 |
| Yakutsk | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| Republic of North Ossetia-Alania | |
| Vladikavkaz | 1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Republic of Tatarstan | |
| Almetyevsk, Zelenodolsk, Nizhnekamsk | 1,3 |
| Bugulma, Leninogorsk, Chistopol | 1 |
| Elabuga | 1,2 |
| Kazan | 2 |
| Naberezhnye Chelny | 1,7 |
| Other cities and towns | 1,1 |
| Tyva Republic | |
| Kyzyl | 0,6 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| Udmurt republic | |
| Votkinsk | 1,1 |
| Glazov, Sarapul | 1 |
| Izhevsk | 1,6 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| The Republic of Khakassia | |
| Abakan, Sayanogorsk, Chernogorsk | 1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| Chechen Republic | 0,6 |
| Chuvash Republic | |
| Kanash | 1,1 |
| Novocheboksarsk | 1,2 |
| Cheboksary | 1,7 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Altai region | |
| Barnaul | 1,7 |
| Biysk | 1,2 |
| Zarinsk, Novoaltaisk, Rubtsovsk | 1,1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Transbaikal region | |
| Krasnokamensk | 0,6 |
| Chita | 0,7 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| Kamchatka Krai | |
| Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky | 1,3 |
| Other cities and towns | 1 |
| Krasnodar region | |
| Anapa, Gelendzhik | 1,3 |
| Armavir, Sochi, Tuapse | 1,2 |
| Belorechensk, Yeisk, Kropotkin, Krymsk, Kurganinsk, Labinsk, Slavyansk-on-Kubani, Timashevsk, Tikhoretsk | 1,1 |
| Krasnodar, Novorossiysk | 1,8 |
| Other cities and towns | 1 |
| Krasnoyarsk region | |
| Achinsk, Zelenogorsk | 1,1 |
| Zheleznogorsk, Norilsk | 1,3 |
| Kansk, Lesosibirsk, Minusinsk, Nazarovo | 1 |
| Krasnoyarsk | 1,8 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Perm region | |
| Berezniki, Krasnokamsk | 1,3 |
| Lysva, Tchaikovsky | 1 |
| Permian | 2 |
| Solikamsk | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 1,1 |
| Primorsky Krai | |
| Arsenyev, Artem, Nakhodka, SpasskDalniy, Ussuriysk | 1 |
| Vladivostok | 1,4 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Stavropol region | |
| Budennovsk, Georgievsk, Essentuki, Mineralnye Vody, Nevinnomyssk, Pyatigorsk | 1 |
| Kislovodsk, Mikhailovsk, Stavropol | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Khabarovsk region | |
| Amursk | 1 |
| Komsomolsk-on-Amur | 1,3 |
| Khabarovsk | 1,7 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Amur region | |
| Belogorsk, Svobodny | 1,1 |
| Blagoveshchensk | 1,6 |
| Other cities and towns | 1 |
| Arhangelsk region | |
| Arkhangelsk | 1,8 |
| Kotlas | 1,6 |
| Severodvinsk | 1,7 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,85 |
| Astrakhan region | |
| Astrakhan | 1,4 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Belgorod region | |
| Belgorod | 1,3 |
| Gubkin, Stary Oskol | 1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Bryansk region | |
| Bryansk | 1,5 |
| Klintsy | 1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Vladimir region | |
| Vladimir | 1,6 |
| Gus-Khrustalny | 1,1 |
| Moore | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 1 |
| Volgograd region | |
| Volgograd | 1,3 |
| Volzhsky | 1,1 |
| Kamyshin, Mikhailovka | 1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Vologda Region | |
| Vologda | 1,7 |
| Cherepovets | 1,8 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Voronezh region | |
| Borisoglebsk, Liski, Rossosh | 1,1 |
| Voronezh | 1,5 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Ivanovo region | |
| Ivanovo | 1,8 |
| Kineshma | 1,1 |
| Shuya | 1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Irkutsk region | |
| Angarsk | 1,2 |
| Bratsk, Tulun, Ust-Ilimsk, Ust-Kut, Cheremkhovo | 1 |
| Irkutsk | 1,7 |
| Usolye-Sibirskoye | 1,1 |
| Shelekhov | 1,3 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Kaliningrad region | |
| Kaliningrad | 1,1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Kaluga region | |
| Kaluga | 1,2 |
| Obninsk | 1,3 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Kemerovo region | |
| Anzhero-Sudzhensk, Kiselevsk, Yurga | 1,2 |
| Belovo, Berezovsky, Mezhdurechensk, Osinniki, Prokopyevsk | 1,3 |
| Kemerovo | 1,9 |
| Novokuznetsk | 1,8 |
| Other cities and towns | 1,1 |
| Kirov region | |
| Kirov | 1,4 |
| Kirovo-Chepetsk | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Kostroma region | |
| Kostroma | 1,3 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Kurgan region | |
| Mound | 1,4 |
| Shadrinsk | 1,1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| Kursk region | |
| Zheleznogorsk | 1 |
| Kursk | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Leningrad region | 1,3 |
| Lipetsk region | |
| Dace | 1 |
| Lipetsk | 1,5 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Magadan Region | |
| Magadan | 0,7 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| Moscow region | 1,7 |
| Murmansk region | |
| Apatity, Monchegorsk | 1,3 |
| Murmansk | 2,1 |
| Severomorsk | 1,6 |
| Other cities and towns | 1,2 |
| Nizhny Novgorod Region | |
| Arzamas, Vyksa, Sarov | 1,1 |
| Balakhna, Bor, Dzerzhinsk | 1,3 |
| Kstovo | 1,2 |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 1,8 |
| Other cities and towns | 1 |
| Novgorod region | |
| Borovichi | 1 |
| Velikiy Novgorod | 1,3 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Novosibirsk region | |
| Berdsk | 1,3 |
| Iskitim | 1,2 |
| Kuibyshev | 1 |
| Novosibirsk | 1,7 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Omsk region | |
| Omsk | 1,6 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Orenburg region | |
| Buguruslan, Buzuluk, Novotroitsk | 1 |
| Orenburg | 1,7 |
| Orsk | 1,1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Oryol Region | |
| Livny, Mtsensk | 1 |
| Eagle | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Penza region | |
| Zarechny | 1,2 |
| Kuznetsk | 1 |
| Penza | 1,4 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Pskov region | |
| Velikie Luki | 1 |
| Pskov | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Rostov region | |
| Azov | 1,2 |
| Bataysk | 1,3 |
| Volgodonsk, Gukovo, Kamensk-Shakhtinsky, Novocherkassk, Novoshakhtinsk, Salsk, Taganrog | 1 |
| Rostov-on-Don | 1,8 |
| Mines | 1,1 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Ryazan Oblast | |
| Ryazan | 1,4 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Samara Region | |
| Novokuybyshevsk, Syzran | 1,1 |
| Samara | 1,6 |
| Tolyatti | 1,5 |
| Chapaevsk | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Saratov region | |
| Balakovo, Balashov, Volsk | 1 |
| Saratov | 1,6 |
| Engels | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Sakhalin region | |
| Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | 1,5 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Sverdlovsk region | |
| Asbest, Revda | 1,1 |
| Berezovsky, Verkhnyaya Pyshma, Novouralsk, Pervouralsk | 1,3 |
| Verkhnyaya Salda, Polevskoy | 1,2 |
| Ekaterinburg | 1,8 |
| Other cities and towns | 1 |
| Smolensk region | |
| Vyazma, Roslavl, Safonovo, Yartsevo | 1 |
| Smolensk | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,7 |
| Tambov Region | |
| Michurinsk | 1 |
| Tambov | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Tver region | |
| Vyshny Volochek, Kimry, Rzhev | 1 |
| Tver | 1,5 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,8 |
| Tomsk region | |
| Seversk | 1,2 |
| Tomsk | 1,6 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Tula region | |
| Aleksin, Efremov, Novomoskovsk | 1 |
| Tula | 1,5 |
| Uzlovaya, Shchekino | 1,2 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Tyumen region | |
| Tobolsk | 1,3 |
| Tyumen | 2 |
| Other cities and towns | 1,1 |
| Ulyanovsk region | |
| Dimitrovgrad | 1,2 |
| Ulyanovsk | 1,5 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Chelyabinsk region | |
| Zlatoust, Miass | 1,4 |
| Kopeisk | 1,6 |
| Magnitogorsk | 1,8 |
| Satka, Chebarkul | 1,2 |
| Chelyabinsk | 2,1 |
| Other cities and towns | 1 |
| Yaroslavl region | |
| Yaroslavl | 1,5 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,9 |
| Moscow | 2 |
| Saint Petersburg | 1,8 |
| Sevastopol | 0,6 |
| Jewish Autonomous Region | |
| Birobidzhan | 0,6 |
| Other cities and towns | 0,6 |
| Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 0,8 |
| Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra | |
| Kogalym | 1 |
| Nefteyugansk, Nyagan | 1,3 |
| Surgut | 2 |
| Nizhnevartovsk | 1,8 |
| Khanty-Mansiysk | 1,5 |
| Other cities and towns | 1,1 |
| Chukotka Autonomous Okrug | 0,6 |
| Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | |
| New Urengoy | 1 |
| Noyabrsk | 1,7 |
| Other cities and towns | 1,1 |
| Baikonur | 0,6 |
If the owner of the car is a foreigner and has temporarily entered the territory of Russia, then a single territorial coefficient of 1.7 is applied to him.
For which traffic violations will the cost of compulsory motor liability insurance increase?
Increased insurance prices await drivers who:
- Have had their driver's license revoked for drunk driving;
- Violated traffic rules, resulting in harm to the life and health of another driver or passengers;
- Refuse to undergo a medical examination;
- Leaving the scene of an accident;
- Have been repeatedly cited for running red lights;
- Exceeded the speed limit by more than 60 km/h;
- They drive into the oncoming lane.
If OSAGO is unlimited, then violations of the car owner will be taken into account.
In addition to traffic violations, the insurance company may pay attention to other circumstances:
- Vehicle age;
- Car mileage;
- Having children in the car;
- Installation of telematics devices on a car and others.
Read more: What traffic violations affect the cost of compulsory motor liability insurance in 2020
KBM
The bonus-malus coefficient also remains unchanged, and an increase in compulsory motor liability insurance in this part is not expected until at least the end of 2019, but from January 1, 2021, only the “cosmetic part” changes - the name of the accident-free driving class will not be used, but simply indicated coefficient.
Was:
Became:
Calculate the cost of your MTPL policy
Latest amendments
The purchase of a compulsory motor liability insurance policy is controlled by law. All changes to the insurance system are also being introduced officially. The last time innovations occurred was in September.
Damage is compensated in the event of a collision of several vehicles at once. The right to receive compensation applies to all owners of an online compulsory motor liability insurance policy, regardless of the date the insurance transaction was concluded. The European protocol, which is drawn up in the absence of traffic police officers, also continues to operate. Resorting to this method of recording damage is permitted only in specific cases.
If the OSAGO policy was issued later than April 28, 2021, it is subject to natural compensation in the form of repair work.
Increasing the cost of an unlimited OSAGO policy
According to the coefficient of the number of persons admitted to management, an increase in the insurance rate is also expected, but only if your policy is unlimited.
| Limited or unlimited OSAGO policy | The coefficient was | The coefficient has become |
| Limited | 1 | 1 |
| Unlimited | 1,8 | 1,87 |
And for legal entities, the policy limitation coefficient is the same - 1.8.
Registration of compulsory motor liability insurance for legal entities
What does having an MTPL policy provide for legal entities:
- Uninterrupted operation of the company's fleet
- No expenses such as paying fines for not having a compulsory motor liability insurance policy
- In the event of an insured event, financial expenses, within the framework of the MTPL agreement, will be paid by the insurance company
- If an organization complies with the norms of current legislation, then this raises the company’s rating, increases the company’s development potential and the number of partners willing to interact and cooperate with such an organization, and as a result, leads to an increase in the company’s profits.
Increasing the age and experience coefficient
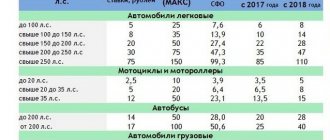
It is this part of calculating the cost of compulsory motor liability insurance that has undergone serious changes. And an increase here is also to be expected. Changes have occurred in terms of gradation of age and experience - if previously there were only 2 of them: younger and older than 22 years, less and more than 3 years of experience, now there will be more variations.
Was:
| Age and experience of drivers | Coefficient |
| Age up to 22 years and experience up to 3 years | 1,8 |
| Age over 22 years and experience up to 3 years | 1,7 |
| Age up to 22 years and experience more than 3 years | 1,6 |
| Age over 22 years and experience more than 3 years | 1 |
And here are the new coefficients based on the age and length of service of eligible drivers.
Something else useful for you:
- How much does it cost to include a driver in MTPL insurance?
- Changes in the rules for drawing up the European protocol from September 13, 2019
- Is it possible to register a car with the MFC today and how? Instructions
How to calculate the price of a policy in 2021 online using a calculator
So that drivers can make an informed choice and purchase only profitable compulsory motor vehicle liability insurance, calculators have been created on the Internet that calculate prices in real time. They work online according to the following simple principle:
- The car owner enters the requested data (indicates the type of car, registers his experience as a driver, etc.).
- The user waits for the calculator to perform the calculation online and sort all the options found.
- The motorist views all market offers in a convenient manner and makes a choice online.