Young drivers often have many questions that somehow never even occurred to them before, when their whole life was spent on two legs. One of the most common - what is the difference between a single dividing strip and a double solid one?
Concept of double and single solid lines
Some drivers face questions about the median lines. Even after completing the courses and having learned all the rules, car enthusiasts do not fully understand the difference between the two concepts. The problem lies in the minimum amount of time allocated for this topic.
Note the difference between the two restrictions:
- Single line - used for marking roads and highways where there are only two lanes for multi-directional traffic (one in each direction).
- Double line – used on wide highways and city roads with four or more lanes. In most cases, such lines can be found on country roads and wide city roads, which provide several oncoming and passing lanes.
Wide highways with several oncoming lanes can significantly increase the space for overtaking, detours and other maneuvers.
This is interesting: 3 violations for which inspectors often punish more severely than expected
Is it possible to cross a solid line?
Despite the ban on driving into oncoming traffic, there may also be certain exceptions. The driver will not receive a fine or lose his license if he is forced to drive into oncoming traffic. For example, its lanes became inaccessible due to a truck accident that completely blocked the road. But here it is also important to consider whether there is a curb. If there is one, you need to continue moving exclusively along it.
If there are repair roads in the lane, does that mean that driving into oncoming traffic is also allowed, since it is forced? New temporary markings are being created in front of repair roads. It is impossible not to notice it, as it is yellow. The repair work itself also cannot be ignored, since appropriate signs, including those with arrows, are required to be placed on the road section. They let the driver know how to continue driving. There will be a detour diagram. All this also applies to roads with both single and double solid roads.
When to use single markup
One of the variations of road markings is single marking, or single solid line, or 1.1 marking.
Single markings are placed not on the edge of the roadway, but exclusively inside it.
Markup 1.1. used in four variants:
For the purpose of marking traffic lanes on roads with several lanes in both directions (two or three)
A single solid line separates two-lane and three-lane roads to separate traffic flows in different directions.
On a three-lane road, such markings also prohibit driving into oncoming traffic and indicate that you should only move in your own lane.
In addition, single markings are drawn on dangerous sections of the road:
- sharp turns when visibility is limited;
- approaching intersections, railroad crossings, pedestrian crossings, or bicycle paths;
- with a lane for minibuses or taxis when access to it is prohibited.
A single line is placed to indicate traffic on a road with 2 and 3 lanes in the same direction
Another quite common case of using a single solid line is when it is applied to a road with a large number of stripes to designate a lane of traffic in a single direction. At the same time, vehicles are prohibited from changing from one lane to another when it is unsafe to do so.
Also, the need for markings 1.1 arises when indicating dangerous sections of the road.
Marking 1.1 for marking parking areas
Such a line is placed on special sites that are intended for parking one vehicle, as well as in parking lots near the sidewalk.
In this case, the markings highlight the very “framework” within which you need to park your car. The driver must follow the parking rules and not leave the car across the designated parking space.
Otherwise, he will grossly violate the rules and, at best, an administrative penalty will be imposed on him.
“Single continuous” for areas where entry is prohibited
A single line is also used in very specific situations: to limit a safe island, a directional island, and other situations if there is a need to prohibit entry to such areas.
What is the difference between solid and double solid?
There is also a double line, where one side is broken, which means that it can only be crossed on the side where the line is not solid.
Let's first refresh our memory of the relevant paragraph of the traffic rules. Markings on the road are discussed in detail in Appendix 2 to the Rules of the Road entitled “Road markings and their characteristics.” A single continuous marking “1.1” separates traffic flows in opposite directions - it is applied on roads that have one lane in each direction.
The law also directly provides for a situation where a driver, who has previously been punished for driving into oncoming traffic, again commits a similar violation. Then waiting for him:
- withdrawal of rights for one year if the violation was noticed by a traffic police officer;
- a fine of 5,000 rubles if the actions of a motorist became known through video recording.
Everything is quite simple here. A single solid line is applied on roads with two lanes, and a double solid line is applied on wide highways and avenues where the number of lanes is more than four. In other words, where there are two or more lanes for traffic in each direction, there should be a double solid one.
Crossing a solid marking line is prohibited, including when making a U-turn or turning. The penalty will be the same as in the case of crossing the line when overtaking - 1000-1500 rubles. To turn or turn around, you need to find the break line and perform the maneuver. These gaps are located at intersections, and on highways they are even marked with special signs.
If the road is double solid, it means you are driving on a highway with at least four lanes (and there may be more). In this case, there are at least two oncoming lanes.
According to traffic rules, marking 1.11 is allowed to cross only by those drivers on whose side there is a broken line. In this case, returning from the “solid” side is possible when overtaking or detouring.
It is designed to separate the flow of cars moving in different directions in two-way traffic. Double markings are found on wide roads where the lanes are more than 375 cm.
Sometimes simple provisions of the rules lead motorists to a state of confusion. For example, why, instead of one white line on the roads, do they draw two parallel ones at once? If you cross one, it is fraught with deprivation of rights. What is the second one?
From the point of view of the Administrative Code, is there a difference in the number of marking lines
There is practically no significant difference between single solid and double. Markings 1.1 are drawn on roads with no more than 2 lanes, and markings 1.3 on roads with several lanes in both directions.
Crossing a double marking line does not mean that the penalty will be double the fine. In the traffic rules there is no such concept as “crossing a single or double continuous marking line”, there is only “entering the lane of oncoming traffic.” That is, crossing a single or double solid line indicates entering the oncoming lane.
It is strictly forbidden to cross both of these markings. Even if you want to make a maneuver such as overtaking or you need to go around an obstacle.
For such a violation, the driver is punished with a fine of five thousand rubles or deprivation of the right to drive a vehicle for a period of 4 to 6 months. If the violation is repeated, the deprivation will be for a year.
When making a U-turn or turning, crossing a single solid or double solid line, it is punishable by a fine of 1 thousand to 1.5 thousand rubles.
Turning, turning around and entering the oncoming lane is allowed only if the solid line has turned into a broken line, and if we are talking about a double solid line, but the dotted line should be on your side of the road.
All landmark lines on roads are invented and written down for a reason. In no case should they be ignored, and every driver, pedestrian or cyclist should know what they mean and how to behave in a given situation, then everyone will be able to protect themselves and other people from road accidents and reduce the risk of an accident.
What is the difference between one solid and double.
Among motorists, there is a kind of joke with some truth about two solid ones.
Supposedly, one solid line warns that overtaking is prohibited, but two solid lines mean a strict prohibition on overtaking. This is really more of a joke, or rather just a joke, because the two solid ones have a real purpose. And this is not at all a strict prohibition of overtaking.
There is also an opinion that for crossing two solid lines, the violator will face double punishment. Let's talk about this in more detail.
A little about continuous markings
A solid line (1.1) dividing the roadway into two equal parts warns traffic participants that overtaking is prohibited. More precisely, it prohibits driving into the oncoming lane. Marking number 1.3 has exactly this meaning. 1.3 looks like two solid lines on the road surface.
What are the differences? The fact is that one continuous lane is used on roads with only two, or maximum three, lanes. Two solid lines separate multi-lane traffic (more than three lanes), more precisely, starting from two lanes in one direction.
A double solid line divides multi-lane traffic into two equal parts. For example, three lanes in one direction, three in the other. It is the two solid lines that clearly delimit the movement of who goes in which direction and in which lane.
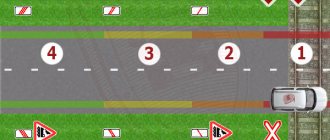
Another purpose of the double solid is the ability to make a safe turn. For example, an allowed left turn will be highlighted with a dashed line on the left, while the right line will still be solid.
This is a signal to the driver to turn left. The same is true on the right side. This is the same as a broken line on one solid line.
It is then that you can overtake or make a U-turn into another lane. The main thing at this point is to pay attention to road signs. Suddenly there is some sign prohibiting anything on this section of the road.
What is the penalty for crossing solid lines in any quantity? Probably now, after explaining the purpose of continuous markings, it became clear that the punishment is equally severe. The key word here is “same.”
According to Article 12.15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses (4 hours), for crossing a solid road or two solid roads, a motorist will be punished in the form of fines (5,000 rubles). But that's not the worst thing. For this offense, the driver may even lose his license for a period of 4 to 6 months.
This is the case when the violation was recorded by traffic police officers. Such a violation, by the way, can also be recorded by traffic cameras. In this case, the violator does not face deprivation of rights. There will only be a fine. This point is specified in Article 28.6 (3h) and 4.1 (3.1h).
The most important thing from all of the above is the conclusion. Whatever the punishment for crossing solid roads in any quantity, this is a serious violation of traffic rules.
Such a violation can lead to serious consequences, including a car accident. It’s not for nothing that solid lines indicate a ban on maneuvering in these sections of roads.
If the article was useful to you and it doesn’t bother you, please give it a thumbs UP and subscribe to the channel, this is IMPORTANT for us!
Purpose of different types of markup
In order to understand, you need to understand in which cases one continuous line is applied to the road surface, and in which – two. Both types of lines are regulated by Appendix 2 to the Traffic Regulations. The first markup option is numbered 1.1, and the second is numbered 1.3.
A single solid line (1.1) is designed to separate traffic flows moving in opposite directions. In addition, it marks the boundaries of lanes in dangerous sections of the roadway, as well as the edge of the roadway and parking spaces.
Double continuous markings (1.3), like single ones, serve to separate traffic flows moving in opposite directions. It is only used mainly on roads with four or more lanes. Marking 1.3 is applied to a two- or three-strip fabric if the width of the stripes exceeds 3.75 m.
So we see that the basic function of these two types of lines is the same. Exactly what marking will be applied depends only on the number of stripes and their width.
Double solid line according to traffic rules and punishment for crossing it
This type of horizontal marking is applied in the center of the road surface in the form of two parallel solid white stripes. Crossing this marking, in accordance with current legal regulations of traffic rules, is strictly prohibited. Such violations are punished quite severely, including deprivation of rights.
Since moving in the oncoming lane poses a serious threat to the health and life of road users, driving beyond the double dividing stripes is punishable by a fine of up to five thousand rubles, or deprivation of driving license for up to six months.
The maneuver is considered acceptable in the following cases:
- when turning or overtaking through a double solid road, if there are permitting signs on this section of the road that give drivers priority over road markings;
- if the driver of the vehicle begins a maneuver to get ahead of the vehicle in a permitted area, but is forced to end in an area that prohibits crossing the markings.
Regarding the last case, it is worth noting that immediately after completing the started maneuver, the car must change lanes. According to current traffic regulations, such actions should not be regarded as a violation. However, in practice the opposite often happens.
Exceptions to the rules
Crossing or hitting a double solid road is not punishable by traffic rules if:
- The maneuver was caused by extreme necessity; the driver in a risky situation could not do otherwise. Such actions are considered justified if the actual damage has become less than the prevented damage.
- Lack of markings in the correct place or their poor condition. In this case, the driver will have to prove that he did not know about the violation of the rules. Photos from the scene or dashcam footage may be useful in court.
What are the consequences of an unpaid fine?
If the car owner refuses to pay the fine, he may be subject to administrative arrest for 15 days or sent to correctional labor for 50 hours. Another measure is to double the previously issued fine.
So, crossing a double solid marking line can cost the car owner from 500 to 5000 rubles, the final amount depends on the degree of the offense and the presence or absence of aggravating circumstances. The maximum period for which a driver can become a pedestrian for such an offense is six months, but if a traffic violation is recorded by an automatic camera, he will not have to part with his license.
Automatic registration of an offense
Cases of offenses on roads with double solid roads are automatically recorded. The practice of using photo and video surveillance cameras began in 2008. Cameras installed permanently send data to information centers, where they are processed and, if violations of the rules are detected, letters are sent to car owners informing them of the imposition of a fine. They cannot deprive rights based on data from automatic cameras.
The technical base is constantly updated, devices have been put into operation that can monitor traffic violations even in the dark, as well as control traffic lights and barriers remotely. However, cases of false alarms or failure to clearly record the license plate number of the offender still occur to this day.
Traffic police inspectors on the roads use mobile systems, sometimes radars with video recording. In this case, a diagram of the place where the administrative offense was committed is drawn up, the marking line and the vehicle traffic pattern are indicated. This scheme is an addition to the protocol on an administrative offense. It, according to Order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs No. 664, paragraph 154, is not mandatory. If available, the diagram is submitted to the court along with the rest of the case materials.
The driver must check if there are any errors in the traffic diagram. In case of disagreement, he can draw up his own scheme and petition for its use in court. You can also take photographs of the scene and bring in witnesses.
How to appeal a fine?
A driver who has received a fine for crossing a double line and thus violated traffic rules has the right to appeal it in court or by contacting the leadership of the local traffic police. Help for an appeal may include:
- Unclear markings. Photographs will help confirm this fact; it is better if they show both the offender’s car and the traffic police vehicle.
- Markings applied in violation of the rules. A solid line should be preceded by a dashed line, and between them there should be a section of the road with short dashed strokes that help the driver orient himself and prepare for the start of the solid line. If there is no such crossing, the road is marked in violation of GOST, it is better to record this fact in a photo or video.
- The fact of a forced violation, for example, to prevent an accident.
- Driving is not the owner of the car, but another driver. The fact must be confirmed by a document, for example, a power of attorney to drive a car. In this case, the offender will pay the fine, not the owner of the car.
- Error in identifying vehicle number. A fairly common case with automatic fixation. To refute, you need to present your own state sign.
Definition
Marking lines on roads serve to divide it into several parts and are painted with white or yellow paint. If a single line is intended to divide the vehicle traffic area into two parts, in which traffic occurs in different directions, then a double continuous line according to traffic regulations is used for similar purposes, but with some features. It is necessary to delimit oncoming traffic flows:
- if there are 4 or more lanes on the road;
- There are less than 4 lanes on the road, but each of them is more than 3 m 75 cm wide.