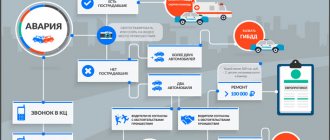
Traffic regulations define pedestrians as full road users. If the driver does not give the pedestrian priority or hits him, he will be subject to administrative or criminal penalties. The current legislation is trying in every possible way to protect the rights of people crossing the roadway, because they are the most vulnerable road users. As a rule, it is the pedestrian who is most often seriously injured in an accident. And in some cases they turn out to be incompatible with life.
The insurance company of the person responsible for the accident pays the damage to the victim. To do this, the motorist must have a compulsory motor liability insurance policy. Moreover, the victim receives compensation regardless of the nature of the injuries and their severity. Any damage incurred as a result of the accident is compensated. Moreover, you can receive not only reimbursement of funds spent on treatment. Expenses for the period during which the victim was unable to work are also paid.
The pedestrian will not receive compensation only if he himself is the culprit of the accident. In such situations, a citizen may be required to pay the costs of the driver whose vehicle was damaged in the accident.
There was an accident with a pedestrian: what to do?
An accident involving a pedestrian is the most unpleasant situation for a motorist. Moreover, an accident can occur even if the driver complied with the speed limit and did not violate traffic rules. Most often, pedestrians get into accidents when they want to cross the road in the wrong place.
If it was not possible to avoid a collision with a pedestrian, the motorist must do the following:
- Stop the car and turn off the engine. It is necessary to turn on the hazard warning lights and place a corresponding sign on the road.
- The pedestrian must be given first aid. It should be moved or removed from the roadway so that it does not fall under the wheels of other vehicles.
- We call traffic police officers and an ambulance to the scene. Even if the pedestrian refused medical help, an ambulance must be called.
- Wait for the inspectors to arrive. The motorist has no right to leave the scene of the accident. This is allowed only in one case, if the driver decided to take the victim to the hospital himself. Then he is obliged to return to the scene of the accident as soon as he is free.
- Take photos and videos of the accident scene. This is especially important if the car of a participant in an accident interferes with the passage of other vehicles. Then the driver must photograph the car and all road objects directly related to the accident. After this, the car must be removed from the roadway.
- Talk to witnesses. It is necessary to record the details of each eyewitness to the accident. Their evidence in court will allow the motorist to avoid punishment if the accident occurred due to the fault of a pedestrian.
- Contact your insurer and lawyer. This stage is not specified in the traffic rules, and therefore is not mandatory. However, an experienced lawyer will allow the driver to avoid punishment or achieve a reduced sentence.
What if the culprit hit and fled?
Here everything is a little more complicated, but judicial practice prescribes something like the following:
- if no information about the car and the culprit is known, then, alas, it will not be possible to receive payment under compulsory motor liability insurance, as well as from anyone else - after all, it is not known who caused harm to the pedestrian,
- if there is information that allows you to identify the car in which the pedestrian was hit, but the driver is not identified because he disappeared, then the insurance of the owner of this car pays.
Article 18 of the Federal Law-40 speaks in favor of the second point, and such a payment will be called “compensatory”. Moreover, there are as many as 2 opinions here, even among traffic lawyers, and it lies in the ambiguity of interpretation of this rule of law:
1. Compensation payment for compensation for harm caused to the life or health of the victim is carried out in cases where insurance compensation under compulsory insurance cannot be made due to: ... c) the unknown person responsible for the harm caused to the victim;
That is, some argue that if neither the car nor any other information about the culprit is known at all, then the pedestrian can still receive such a payment. The latter say that a car cannot be a person, and therefore we are talking specifically about a situation where the driver is not identified. And it is the latter, of course, who are right.
Features of registration of an accident
Traffic police officers are required to record all the circumstances of the accident. However, the motorist must also take photos and videos of the accident scene. You should pay attention to the following nuances:
- position of the car and pedestrian after a collision;
- tread marks on the asphalt;
- damage caused to the car as a result of a collision;
- the condition of the road surface at the scene of the accident (part of the blame can be placed on the road services).
In the settings of your phone or camera, you need to set the function to display the current date and time on photographs.
Moral damage
Compared to damage caused to the health and property of a pedestrian, moral damage (related to the mental and psychological state of the victim) is the most difficult to prove. The main criterion in this case will be evidence from the injured party that it was as a result of the accident that damage was incurred, which subsequently contributed to the development of mental and psychological discomfort.
To prove the existence of moral damage, initially, the pedestrian needs to prove the existence of damage caused to health. To do this, it is necessary to collect the same list of documents that is required to prove damage to the health of a pedestrian.
Having proved physical damage, the injured party will automatically prove moral damage.
The cost of compensation may depend on treatment costs and moral recovery after an accident.
Compensation for damage
If the driver is found guilty of an accident, he will have to pay the victim the following types of compensation:
- For damage to property. If, as a result of a collision, a person’s clothing is torn or a mobile phone is broken, then the cost of these things will have to be reimbursed.
- For harm to health. This includes compensation for funds spent on treatment, as well as payments for temporary disability. For example, if as a result of an accident a citizen was unable to work for some time, then all lost profits are compensated by the person responsible for the incident.
- For moral damage. Such compensation can only be demanded through the courts.
- A one-time payment in the event of the death of the victim.
Accident with a pedestrian: compensation for damage through insurance
A pedestrian has two ways to receive payments for damage caused to him in an accident. File a claim against the car owner or contact the insurer that insured his liability.
In the second case, the victim needs to contact the insurer as soon as possible after the car accident to notify him of the insured event. In this case, he must submit a document (certificate) confirming the fact of the accident, an application requesting payment of compensation and all documents confirming the damage caused to his property and/or health. What kind of documents these are is described above.
The maximum period for reviewing documents by the insurer is 20 days, excluding non-working days. During this period, the insurance company is obliged to either pay compensation or refuse it, justifying its decision.
The insurer knows that if payments or denials do not reach the victim within the allotted time, he will have to pay penalties. This is a good incentive not to procrastinate.
The maximum amounts of compensation for damage are specified in Art. 7 of the Law on Compulsory Motor Liability Insurance. Today they are:
- 500 thousand rubles. – to compensate for harm caused to the health or life of each victim;
- 400 thousand rubles. – when compensating for damage to the property of all victims.
If the actual damage turns out to be greater than the insurance payments, the missing amount can be recovered by filing a lawsuit against the person responsible for the damage caused.
In addition to MTPL insurance, the car owner may have a voluntary insurance agreement. In such cases, the victim is given the right to apply for compensation to the company that has issued voluntary insurance. Moreover, payments with this option may be higher than with compulsory motor liability insurance.
On a note! If the car owner at fault for the accident has not insured his liability at all, or the guilty party has not been identified, it makes sense for the victim to apply for compensation to the Russian Union of Auto Insurers.
How to receive compensation under compulsory motor liability insurance
To receive payments under compulsory motor liability insurance, the victim must have the following documents:
- protocol;
- certificate of accident.
Both documents are drawn up by traffic police inspectors who arrived at the scene of the incident. The report contains the name of the culprit's insurance company and his insurance policy number. These details should be used to receive compensation.
If a pedestrian received serious bodily injury in an accident, the driver will face criminal penalties. Accordingly, the victim will have to submit a resolution to the insurance company to initiate criminal proceedings.
While the victim is being treated at the clinic, his relatives can contact the insurance company’s office and find out what documents should be prepared to receive compensation. This approach will save time.
If a motorist requires treatment as a result of an accident, he should keep all receipts confirming the expenses incurred. These may be receipts for payment for procedures, documents confirming the cost of treatment and accommodation in a sanatorium, etc.
Compensation under compulsory motor liability insurance for damage to health is up to 50 thousand rubles. If this amount is not enough for a person, he has the right to demand the rest of the funds from the person responsible for the accident. If the driver refuses to pay voluntarily, he should go to court.
Accident with a pedestrian: grounds for compensation for damage
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation gives every citizen the right to compensation for damage caused to his property and/or health (clause 1 of Article 1064 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), as well as compensation for moral damage (Articles 151, 1100 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The law classifies vehicles as high-risk vehicles. Clause 1 Art. 1079 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation indicates that responsibility for damage caused by vehicles rests with their owners, who are obliged to compensate pedestrians for damage caused in an accident - regardless of whose fault the accident occurred.
You need to understand that the driver is not always the owner of the vehicle. For example, he can use it under a lease or power of attorney. But in any case, the owner of the car is responsible. There are only three exceptions in which he can be found not responsible for the consequences of an accident: if an event of force majeure occurred (force majeure), the victim deliberately provoked a collision (that is, there was intent), the car was stolen.
In the following, for simplicity of presentation, we will assume that the driver of the car involved in an accident is also its owner.
In a pedestrian accident, compensation for damages depends on the consequences of the accident. The law clearly distinguishes the type of harm caused to a pedestrian as a result of a car accident. It could be:
- property damage;
- harm to health;
- harm to life (death);
- moral harm, that is, physical and mental suffering of the victim.
Each of these cases has its own nuances when obtaining compensation.
Property damage
It is divided into two types - damage and destruction. In the first case, expenses for repairs, expenses for transportation, storage, etc. are subject to compensation. If property is destroyed, the victim can claim compensation for the value that was relevant on the day of the accident.
To prove the fact of property damage, the victim must submit relevant documents.
- A certificate of the fact of an accident issued by a traffic police officer.
- A certificate confirming the victim's ownership of the property.
- Expert opinion on the extent of damage incurred. Payment for the services of the expert himself, confirmed by a receipt, can also be added to it.
- Receipts for payment for transportation, storage and other manipulations with damaged property.
- Documents that confirm the fact and amount of repair costs - payment to repairmen, cost of spare parts, materials, etc.
A certificate of the fact of an accident is required in all cases without exception, so it will not be mentioned in the future.
Harm to health
Compensation for harm to health includes compensation for lost earnings or other income, coverage of treatment costs - expenses for medicines, special food, care, hospital or sanatorium treatment, etc.
Important! Only real expenses are subject to compensation. If treatment and rehabilitation were free, the victim cannot count on monetary compensation.
To receive compensation, the following documents must be submitted:
- medical certificate of disability;
- certificates of average monthly earnings, pensions, business income, etc.;
- documents confirming the costs of treatment: receipts for payment for food, medications, medical services, an extract from the medical history, etc.
Death
Compensation in case of death of the victim consists of two parts.
- Funeral expenses.
- Compensation to persons who were dependent on the deceased. These are mainly children under 18 years of age and disabled people who were related to the deceased and were his dependents. A complete list of such persons is listed in Art. 1088 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
To confirm the fact of the loss of a breadwinner, all dependents must submit the appropriate documents. Their form depends on specific conditions. This could be a certificate from an educational institution, a birth certificate for children, a report on the health status of disabled people, etc.
The fact of expenses for the funeral of a person killed in an accident also requires documentary evidence - checks, receipts, etc.
Moral injury
Moral damage may seem like something ephemeral, but in reality it is simple. It is believed that if harm was caused to your health, then you must have experienced physical and mental suffering. Thus, by proving that damage to health was caused, you automatically prove moral damage.
The amount of compensation for moral damage is determined by the degree of damage caused to the physical and mental health of the victim. Moral damage is confirmed by the same documents as damage to health. The testimony of witnesses is also taken into account.
What to do if the accident was caused by a pedestrian
Often an accident occurs as a result of a pedestrian’s inattention or disregard for traffic rules. If the motorist manages to prove his innocence, he will not have to compensate for the damage suffered by the pedestrian. Moreover, the court may oblige the latter to pay the driver for repairs to his car.
When a pedestrian is at fault for an accident, the driver is exempt from paying fines and cannot be prosecuted. Moreover, the outcome of the accident does not matter. If a pedestrian died due to his own negligence, the driver should not be held responsible for it.
Procedure
Let's consider the situation from the driver's side. Even if the speed limit is observed and the vehicle is in full working order, a pedestrian may suffer:
- If possible, the driver is obliged to provide first aid to the injured person. It should be remembered that transportation to the hospital can lead to complications and end in failure. This is especially true when the spine is damaged. It is advisable to immediately call an ambulance.
- Keep calm. Call a traffic police officer. Do not leave the scene of the incident, prepare personal documents and papers for the car. Wait for special services to arrive. The driver can leave the scene of an accident only if the victim requires immediate medical attention. The main condition will be the absence of other people who can provide it.
- Clear the roadway if the car interferes with the passage of other people. At the same time, record all the details of the accident using video recording. If the car does not interfere with the passage, then everything can be left as is, having first placed an emergency sign on the road.
- Contact a representative of the insurance company or a lawyer you know to get advice on the issues of compensation for health damage to a pedestrian, taking into account specific nuances and details. If you wish, talk to witnesses of the accident with possible recording of conversations. The person should be warned about this fact in advance.
Practice shows that even if there is a problem with the passage of other road users, the location or other details should not be changed. This may be regarded by traffic police officers as falsification of facts or hiding from the scene of an accident.
What documents need to be submitted to the insurance company?
If a person dies as a result of an accident, compensation can only be obtained after his funeral has been organized. The general list of documents should include papers indicating payment for funeral services.
When a family breadwinner dies in an accident, his relatives must prepare the following documents:
- a copy of the death certificate;
- a statement with information about family members of the deceased;
- certificate of disability (if among relatives there are persons with a similar status);
- birth or adoption certificate (for children under 18 years of age at the time of the accident);
- a document confirming that a relative of the deceased is studying at an educational institution;
- certificate of income of the deceased;
- a certificate from the social security authority confirming the fact that one or more relatives of the deceased need care;
- bank details for transferring funds;
- certificate of accident;
- protocol drawn up by the traffic police inspector.
If the amount exceeds 500 thousand?
Everything that is not covered by the MTPL policy is recovered directly from the culprit. To do this, you will have to make copies of the documents listed above, certified by an authorized body: respectively, the traffic police, the forensic medical examination, the court and medical institutions, since you will leave the first copies with the insurance company.
In relation to the culprit of the accident, it is first better to submit a pre-trial demand to his registration address with a list of the contents and a notification of delivery, attaching photocopies of documents confirming your claim. With such a claim, you have the opportunity to recover the amount not covered by its insurance without going to court.
There are also advantages for the culprit himself - if you file a claim in court, he will incur additional expenses in the form of state fees, costs for documents and representation of the plaintiff in court, which are reimbursed by the losing party of the case.
If the culprit ignores the “pre-trial”, then he will have to file a lawsuit at the defendant’s place of residence.
What to do after an accident?
If a pedestrian has been injured in an accident, the following actions must be taken:
- Call medical workers to assist the victim.
- Report the incident to the traffic police.
- If possible, remove the vehicle if it interferes with the movement of other vehicles, or put up a warning triangle.
- Record the data of eyewitnesses, if any, in order to transfer information about them to the traffic police.
- Tell your insurer what happened.
If the driver is able, he should carry out some first aid measures for the victim. These include:
- stopping bleeding using a tourniquet or improvised means;
- splinting a fracture;
- closed cardiac massage, in the absence of a pulse.
But if the driver is not confident in his knowledge and skills, it is best to wait for the ambulance to arrive, since incorrect actions can cause even more harm to the victim. Leaving the scene of an accident is prohibited.
Pedestrian liability
A pedestrian, like any other road user, under some circumstances may well find himself subject to criminal liability, including imprisonment. But in practice, the maximum punishment for a pedestrian for violating traffic rules usually does not exceed 1000 rubles (the maximum administrative fine).
It’s another matter if people were injured as a result of an accident caused by a pedestrian. Then the punishment will be much more serious:
- if harm to health is mild or moderate, you will have to pay a fine of 1,000 to 1,500 rubles;
- in case of causing serious harm to health, the liability is different, within the framework of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (up to 2 years of imprisonment);
- in the event of a fatality caused by a pedestrian, he may face criminal liability in the form of imprisonment for up to 4 years;
- If 2 or more people died in an accident, the term of imprisonment can be increased to 7 years.
Damage to property
Damage caused to property is divided into two types: damage and complete destruction. If parts of the car were damaged in an accident, but it can be restored, then the person responsible for the accident is obliged to compensate the cost of repairs, as well as spare parts.
If the car is completely destroyed in an accident, the injured party has the right to demand compensation from the culprit for the entire cost of the vehicle.
Important! When reimbursing the full value of the vehicle, depreciation costs should be taken into account. That is, when calculating the amount, the cost of the car at the time of the accident is taken into account according to market prices.
To confirm damage has been caused, the injured party must prepare documents that prove this.
These include:
- a certificate from the state traffic inspection, which indicates the occurrence of an accident;
- papers that serve as confirmation of ownership of the car damaged in the accident;
- the results of the examination, which indicates the exact amount of damage caused;
- receipts, checks, orders for payment for tow truck services, parking lots, etc.;
- papers that will serve as proof of the cost of the vehicle repairs;
- checks, receipts, orders for the cost of spare parts used to restore the car.
A document from the State Road Safety Inspectorate regarding the occurrence of an accident is always required without exception. Therefore, without it, the insurance company has the right to refuse to provide payment .